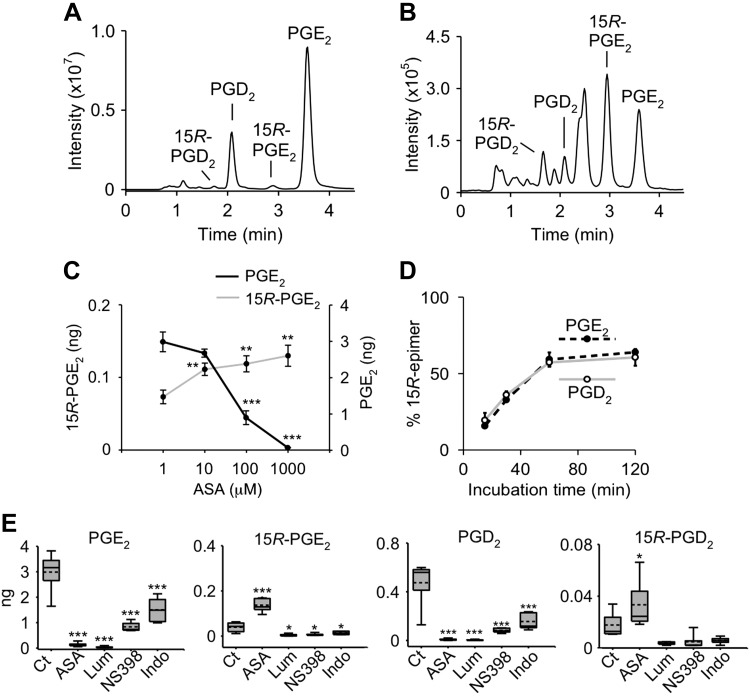
Figure 3.
Effect of aspirin and other inhibitors on PG formation by recombinant COX-2. A, B) SP-LC-MS analysis of reactions of COX-2 (A) and acetylated COX-2 with arachidonic acid (B) monitoring the transition of m/z 351 to 271 (loss of 2 × H2O and CO2) in negative ion SRM mode. C) Dose-response curve of aspirin in the formation of 15R-PGE2 and inhibition of PGE2 by COX-2. D) Relative proportion (%) of 15R-PGE2 and 15R-PGD2 of total PGE or PGD, respectively, as a function of the incubation time with aspirin. E) Formation of PGE2, 15R-PGE2, PGD2, and 15R-PGD2 by COX-2 in a control reaction (Ct) or in the presence of aspirin (ASA), lumiracoxib (Lum), NS-398, or indomethacin (Indo). Reactions were conducted in 100 μl of buffer, and products were quantified by LC-SRM-MS analysis using d4-PGE2 as internal standard. Values are means ± sd (n = 3 independent experiments). **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (statistically significant reduction of PGE2 or increase of 15R PGE2 compared with control).