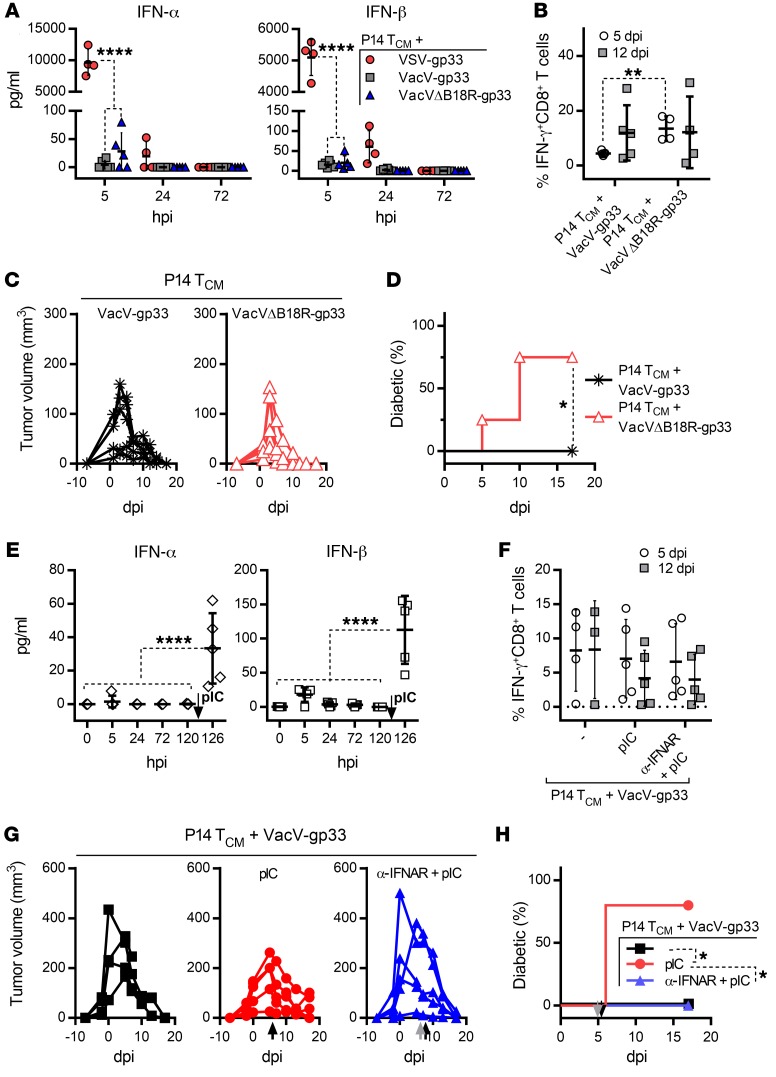
Figure 6. B18R-mediated neutralization of IFN-α/-β decouples tumor regression from autoimmune diabetes but can be overwhelmed by pIC treatment.
(A) Systemic levels of IFN-α and IFN-β detected in plasma samples taken from B16-gp33 tumor–bearing RIP-gp mice at the indicated time point (hours post infection [hpi]) after injection of the VSV-gp33 (n = 4), VacV-gp33 (n = 6), or VacVΔB18R-gp33 (n = 5) component of the combination therapy. (B) gp33-specific CD8+ T cell responses and (C) tumor volume were measured on the indicated dpi in B16-gp33 tumor–bearing RIP-gp mice treated with P14 TCM cells plus VacV-gp33 (n = 5) or P14 TCM cells plus VacVΔB18R-gp33 (n = 4). (D) Percentage of mice that developed diabetes. (E) Systemic levels of IFN-α and IFN-β in plasma samples (n = 5), (F) gp33-specific CD8+ T cell responses, and (G) tumor volume induced by the combination therapy were measured on the indicated day following infection with VacV-gp33 (n = 4). This was followed by pIC treatment on day 5 after infection (120 hpi), as shown by the black arrows in E, G and H (n = 5). An additional group received a bolus of the IFNAR-blocking Ab 2 hours prior to pIC treatment, as shown by the gray arrow in G and H (n = 5). (H) Percentage of mice that developed diabetes. Data for B–D and F–H are representative of 2 independent experiments and are shown as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ****P < 0.0001, by 2-way ANOVA (A and F) or 1-way ANOVA (E) with Holm-Sidak correction for multiple comparisons, 2-tailed Student’s t test (B), and log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test (D and H).