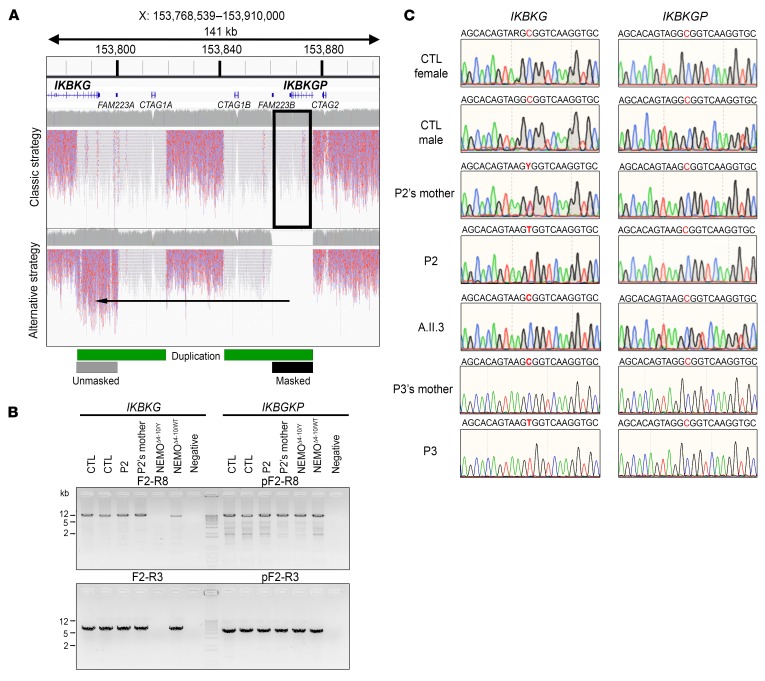
Figure 2. Genomic strategies to identify IKBKG variants.
(A) Comparison of WGS mapping results between the classical and alternative (masking of the IKBKGP locus) strategies. The red/blue reads are the mapped sequences that can be used for variant calls (mappy quality score [MQ] >20), and the gray/white reads are the mapped sequences for which no variant could be called (MQ = 0). The duplicated region is indicated with a green bar and the masked region with a black bar. (B) Specific amplification by PCR of the full-length (top) or partial (bottom) IKBKG locus. gDNA from 2 controls (CTL), a patient (P2) and his mother, and from 2 NEMOΔ4–10 (from 1 male and 1 female patient) SV40 immortalized fibroblast lines was used as the template. (C) IKBKG and IKBKGP DNA sequence electropherograms for controls, SV40-immortalized fibroblasts from a patient (P2) and his mother and a healthy brother (A.II.3), and for the leukocytes from a patient (P3) and his mother.