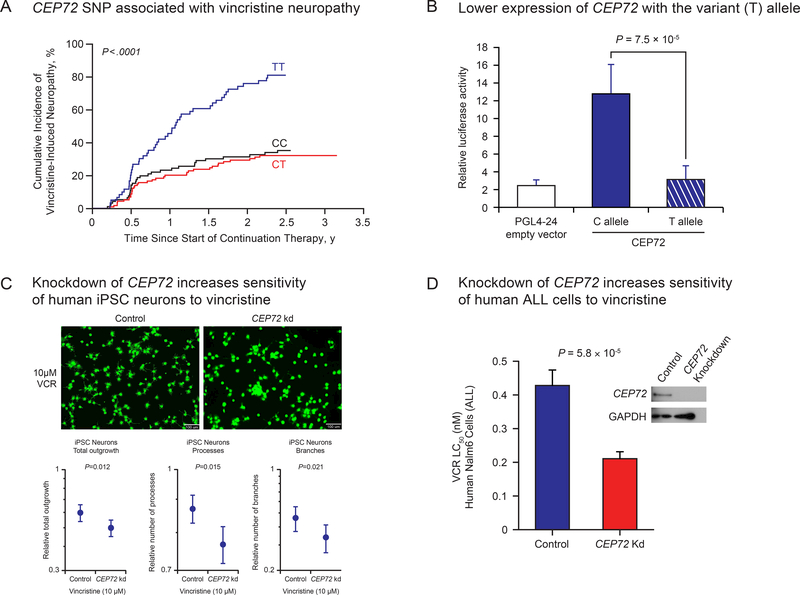
Figure 1.
Association of genetic polymorphism in CEP72 and vincristine-induced peripheral neuropathy. (A) The cumulative incidence of grade 2–4 vincristine-induced peripheral neuropathy as originally discovered in two cohorts of children treated for acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). (B) The CEP72 risk-allele (T at rs924607) leads to low expression of CEP72 as shown by the luciferase activity of the of the CEP72 promoter containing the T allele compared to the C allele. (C) Reduction of CEP72 expression by shRNA in human iPSC neurons increased their sensitivity to vincristine, and (D) reduction in the expression of CEP72 in human ALL cells also increased their sensitivity to vincristine.
Panel A and the images in Panel C appear as they were originally published in Diouf et al., JAMA 20158. Reproduced with permission from JAMA. 2015. 313(8):815–823. Copyright©2015 American Medical Association. All rights reserved.