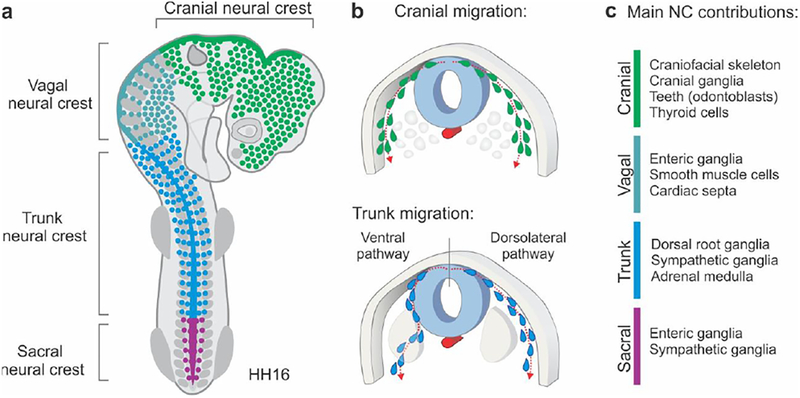
Figure 1. Overview of neural crest subpopulations along the anteroposterior axis.
(A) Diagram of neural crest subpopulations in an HH16 chick embryo. The cranial neural crest subpopulation includes neural crest cells that are formed between the forebrain and the 6th rhombomere (R6) of the hindbrain. The vagal crest is adjacent to the first seven somites. The trunk neural crest spans from the 8th to the 27th somite, while the sacral neural crest is positioned posterior to this boundary. (B) Differences in migratory patterns among neural crest subpopulations. While the cranial neural crest migrates dorsolaterally, the trunk neural crest, which is present adjacent to the developing somites, may take either the dorsolateral or ventral pathway of migration. (C) Major derivatives of neural crest subpopulations. The cranial neural crest gives rise to the craniofacial skeleton and is the only subpopulation possessing ectomesenchymal potential in amniotes. HH: Hamburger and Hamilton developmental stages.