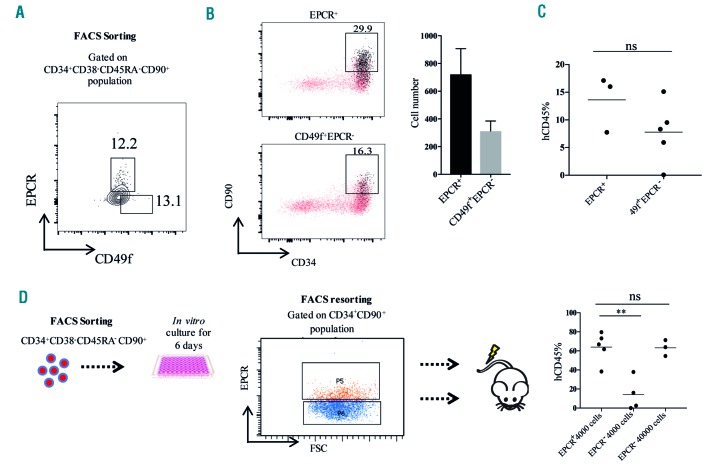
Figure 3.
Endothelial protein C receptor expression in umbilical cord blood hematopoietic stem cells. (A) The gating strategy used to obtain the UCB-derived EPCR+ and 49f+EPCR− populations. (B) To measure the in vitro expansion activity of EPCR+ and CD49f+EPCR− populations, 500 cells from each population were sorted and expanded in serum-free expansion medium (SFEM) supplemented with STF (stem cell factor, FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 ligand and thrombopoietin). Flow cytometric analysis of CD34, CD90 and EPCR expression in the progeny of UCB-derived EPCR+ and CD49f+EPCR- populations is shown. EPCR+ cells are highlighted in black. The experiment was performed in three independent samples in duplicate. (C) To evaluate the in vivo repopulating activity of EPCR+ and CD49f+EPCR− populations, 200 cells from each population were sorted and transplanted into sublethally (300 cGy) irradiated NSG mice and the levels of human cell engraftment in the BM were analyzed after 16 weeks. (D) To evaluate whether EPCR expression enriches for long-term HSC in cultured UCB HSPC, EPCR+ cells (4000/mouse) and EPCR− cells (4000/mouse in one group and 40000/mouse in the second group) derived from CD34+CD90+ population were transplanted into sublethally irradiated NSG mice. At week 16, the frequency of hCD45 cells in BM was evaluated. EPCR: endothelial protein C receptor; UCB: umbilical cord blood; BM: bone marrow; HSPC: hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. **P≤0.01.