Figure 1.
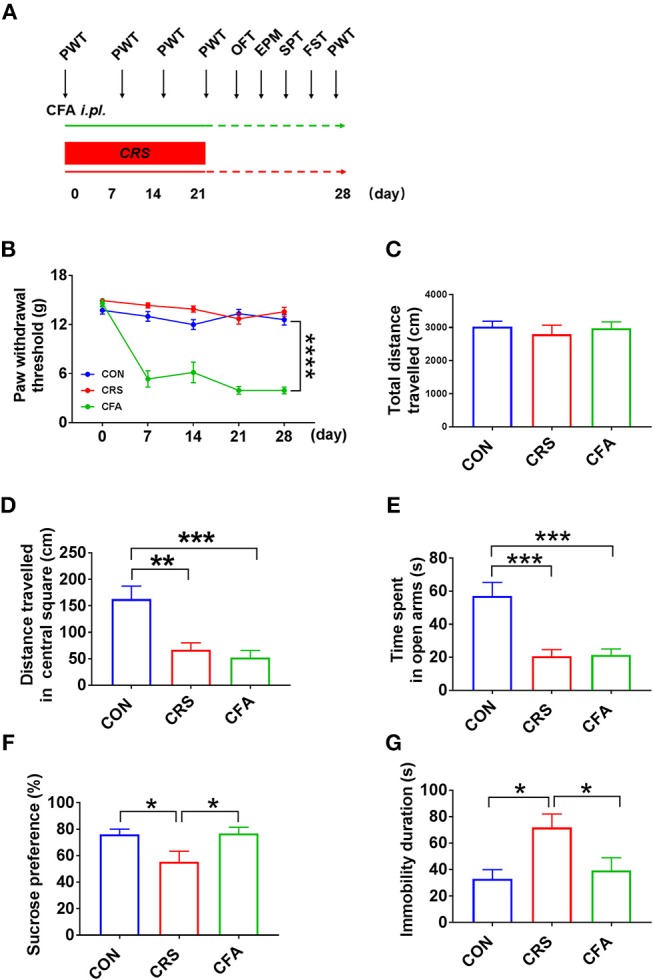
Behavior analyses of CFA-evoked anxiety-like and CRS-evoked depressive behaviors (A) Time schedule of behavioral tests of rats injected with CFA or subjected to CRS for 21 days. (B) A significant decrease in the PWT in CFA-injected rats at 7, 14, 21, and 28 days after injection. CRS did not affect PWT. A repeated-measured analysis of variance (ANOVA), ****p < 0.0001 vs. CON, n = 10 for each group; all graphs represent values in mean ± SEM. (C–G) CRS and CFA did not affect the total travel distance in the OFT (C). Distance traveled in central square in OFT (D) and time spent in the open arms in the EPM test (E) were significantly decreased following CRS or CFA injection; meanwhile, CRS decreased sucrose intake (F) and prolonged immobility time in the FST (G). CFA, complete Freund's adjuvant; CRS, chronic restraint stress; PWT, paw withdrawal threshold; OFT, open field test; EPM, elevated plus maze; SPT, sucrose preference test; FST, forced swim test. N = 9–10 in each group *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 vs. control group (one-way ANOVA). All of the data are presented as mean ± SEM.
