Figure 1.
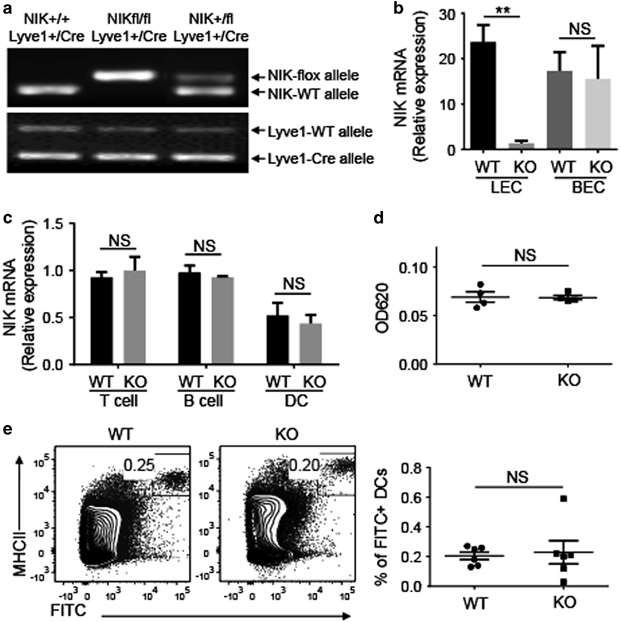
LEC-specific NIK is dispensable for global function of lymphatic vessels. (a) Genotyping PCR analysis of NIK-flox, NIK-WT, Lyve1-Cre and Lyve1-WT alleles using tail DNA to identify wild-type (WT, NIK+/+Lyve1+/Cre), heterozygous (NIK+/flLyve1+/Cre) and homozygous LEC-conditional NIK-KO (NIKLEC-KO, NIKfl/flLyve1+/Cre) mice. (b, c) The qRT-PCR analysis of Nik expression was performed using total RNA from LECs and BECs (b) or T cells, B cells and DCs (c) sorted from WT and NIKLEC-KO (KO) mice by flow cytometry. Data are presented as summary graphs for the expression of Nik normalized to the expression of the housekeeping gene Actb. (d) Measurement of lymph flow in the ear with Evan blue dye. Evan blue dye was injected to the ears of WT and NIKLEC-KO (KO) mice and the remaining dye was extracted 24 h after injection. The amount of extracted dye was determined by measuring the absorbance at 620 nm. (e) Flow cytometry analysis of the frequency of skin-derived DCs (FITC+MHCII+) in iLNs from WT and NIKLEC-KO (KO) mice 18 h after FITC painting. Data are presented as representative plots (left) and summary graphs (right). Data are representative of two independent experiments and are presented as means±s.e.m. BEC, blood endothelial cell; DC, dendritic cell; FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; iLN, inguinal lymph node; KO, knockout; LEC, lymphatic endothelial cell; Lyve1, lymphatic endothelial hyaluronan receptor 1; NIK, nuclear factor-κB-inducing kinase; NS, not significant, qRT-PCR, real-time quantitative PCR; WT, wild type. **P<0.01.
