Fig. 2.
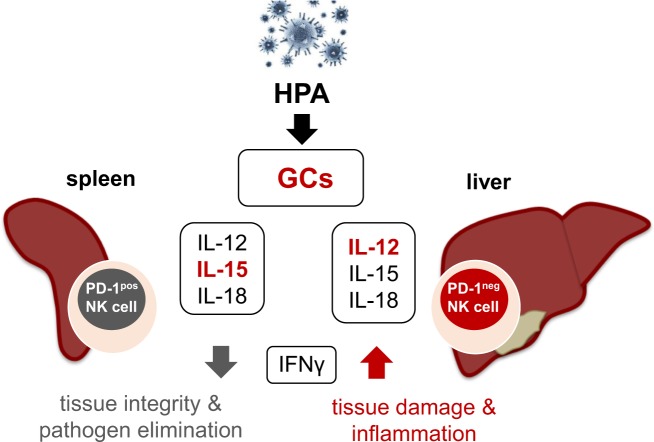
Endogenous GCs and the cytokine microenvironment decide about tissue pathology and pathogen elimination. Viral induction of the HPA leads to secretion of endogenous GCs. The cytokine microenvironment, especially the presence/absence of IL-12 and IL-15, together with the secreted GCs mediate tissue-specific PD-1 expression on splenic NK cells. In the liver, high-IL-12 levels lead to PD-1neg NK cells, whereas elevated IL-15 presence in the spleen activated a high proportion of NK cells to express PD-1 on their surface. Subsequently, PD-1 expression limits the secretion of the pro-inflammatory cytokine interferon gamma (IFN-γ), especially in the spleen, preserving tissue integrity and promoting effective pathogen elimination. In contrast, absence of this pathology preventive pathway leads to high-IFN-γ levels causing severe tissue damage and inflammation. Hence, activation of this neuroendocrine pathway sustains tissue integrity and effective pathogen elimination