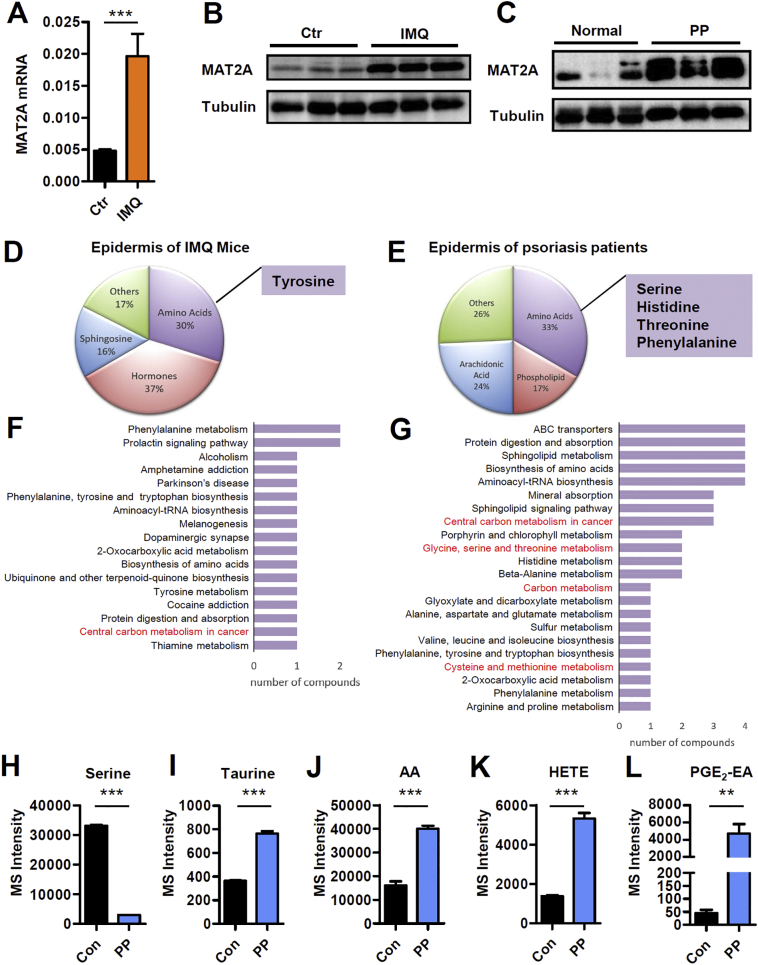
Fig. 7.
MAT2A Expression and Metabolism Profile of Epidermis Derived from IMQ Mice and Psoriasis Patients. (A) qPCR analysis of MAT2A mRNA expression in epidermis of mice treated with blank vehicle control or imiquimod. Significant differences are indicated: two-tailed Student's t-test, n = 9–11 per group (mean ± SEM). (B) Western blotting analysis of MAT2A in epidermis of imiquimod induced mouse model of psoriasis. (C) Western blotting analysis of MAT2A in epidermis of psoriasis patients. (D) The dominant deregulated metabolites in epidermis of lesional skin from imiquimod induced mouse model of psoriasis compared with untreated mice (n = 6). (E) The dominant deregulated metabolites in epidermis of lesional skin from psoriasis patients compared with healthy controls (n = 6). (F) The most changed KEGG pathways involved with amino acids in epidermis of lesional skin from imiquimod mouse model. Those are related to one‑carbon metabolism are marked in red. (G) The most changed KEGG pathways involved with amino acids in epidermis of lesional skin from psoriasis patients. Those are related to one‑carbon metabolism are marked in red. (H-L) One‑carbon metabolism related metabolites in psoriasis patients compared with healthy controls. Significant differences are indicated: **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, two-tailed Student's t-test, n = 6 per group, (mean ± SEM).