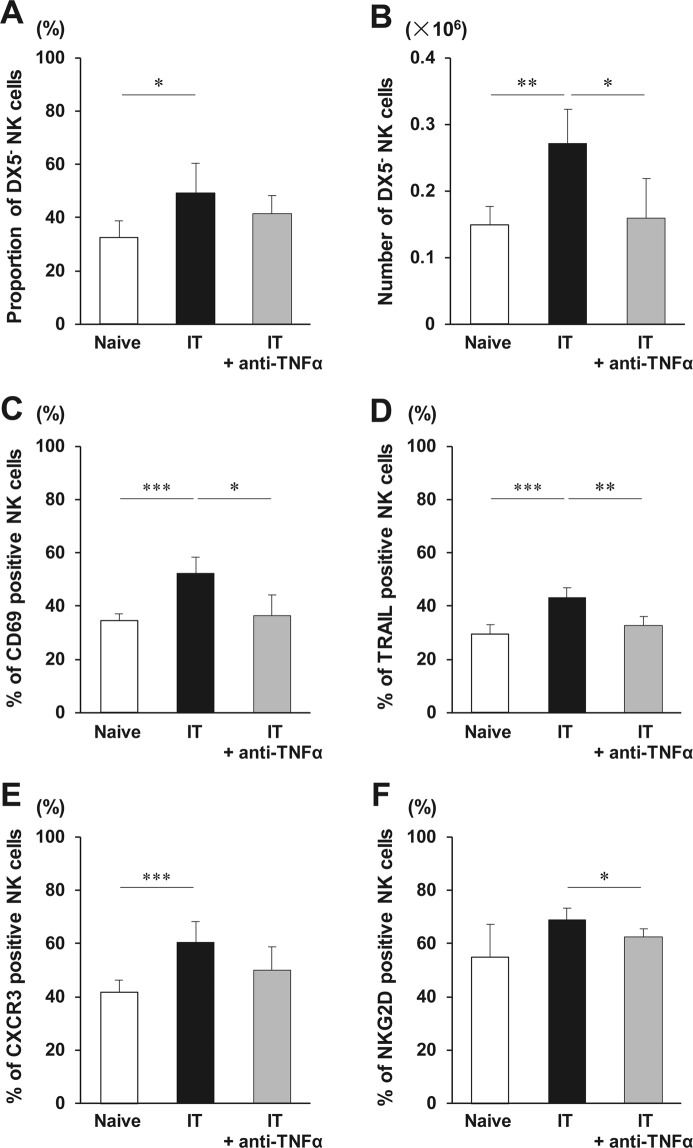
Figure 3.
Phenotypic alterations of liver natural killer (NK) cells early after islet transplantation (IT). C57BL/6 wild-type mice administered PBS or anti-TNF-α antibody were treated with 300 syngeneic islets. Phenotypic alterations of NK cells in the liver were analysed 24 h after intraportal IT. (A,B) Proportion of TCRβ− NK1.1+ DX5− NK cells in total NK cells and the absolute number of DX5− NK cells obtained from the liver of mice that received 300 syngeneic islets, and that were treated or not with anti-TNF-α antibody (naive group, open bar; group that received transplantation, solid bar; group that received islet and anti-TNF-α antibody treatment, gray bar) (n = 5–7). The data in bar graphs are shown as the means ± standard deviation (SD) of 5 independent experiments. *p < 0.05. **p < 0.01. (C–F) Percentages of CD69-, TRAIL-, CXCR3-, or NKG2D positive NK cells in the liver after intraportal IT were analysed with flow cytometry (naive group, open bar; group that received transplantation, solid bar; group that received islet and anti-TNF-α antibody treatment, gray bar) (n = 5–7). The data in bar graphs are shown as the means ± SD of 5 independent experiments. *p < 0.05. **p < 0.01. ***p < 0.001.