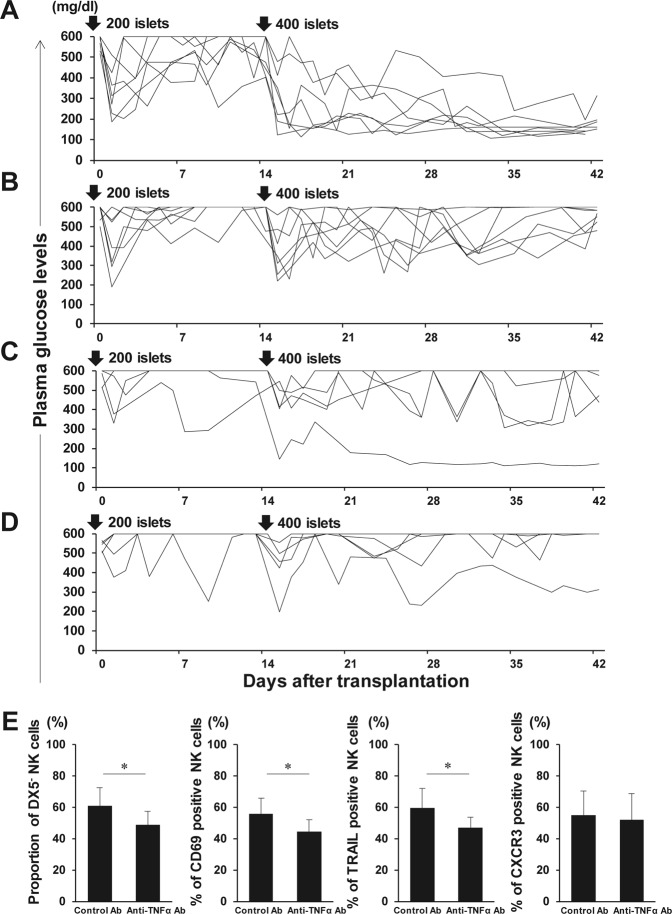
Figure 7.
Graft survival after secondary islet transplantation (IT) with anti-TNF-α antibodies. Syngeneic islet graft survival in diabetic C57BL/6 (B6) mice that were intraportally transplanted with 400 syngeneic islets 14 days after the primary transplantation of 200 syngeneic islets was monitored by measuring the non-fasting plasma glucose level after intraportal IT. Glucose levels less than 200 mg/dL indicated diabetes reversal. Liver TCRβ− NK1.1+ natural killer (NK) cells were harvested at day 42 and analysed with flow cytometry. (A) Diabetic B6 mice were treated with intraperitoneal injection of anti-TNF-α antibodies on days 0, 3, 7, and 10 of each IT (n = 7). Data were collected from 5 independent experiments. (B) Diabetic B6 mice were treated with intraperitoneal injection of normal goat IgG antibodies on days 0, 3, 7, and 10 of each IT (n = 7). Data were collected from 5 independent experiments. (C) Diabetic B6 mice were treated with intraperitoneal injection of anti-TNF-α antibodies on days 0, 3, 7, and 10 of the secondary IT (n = 5). Data were collected from 4 independent experiments. (D) Diabetic B6 mice were treated with intraperitoneal injection of normal goat IgG antibodies on days 0, 3, 7, and 10 of the secondary IT (n = 5). Data were collected from 4 independent experiments. (E) Proportion of DX5− NK cells in total NK cells obtained from IT recipients together with the control or anti-TNF-α antibodies at primary and secondary IT (n = 7). Expression of CD69, TRAIL, and CXCR3 on these cells was analysed. Data are presented as the means ± standard deviation of 5 independent experiments. *p < 0.05.