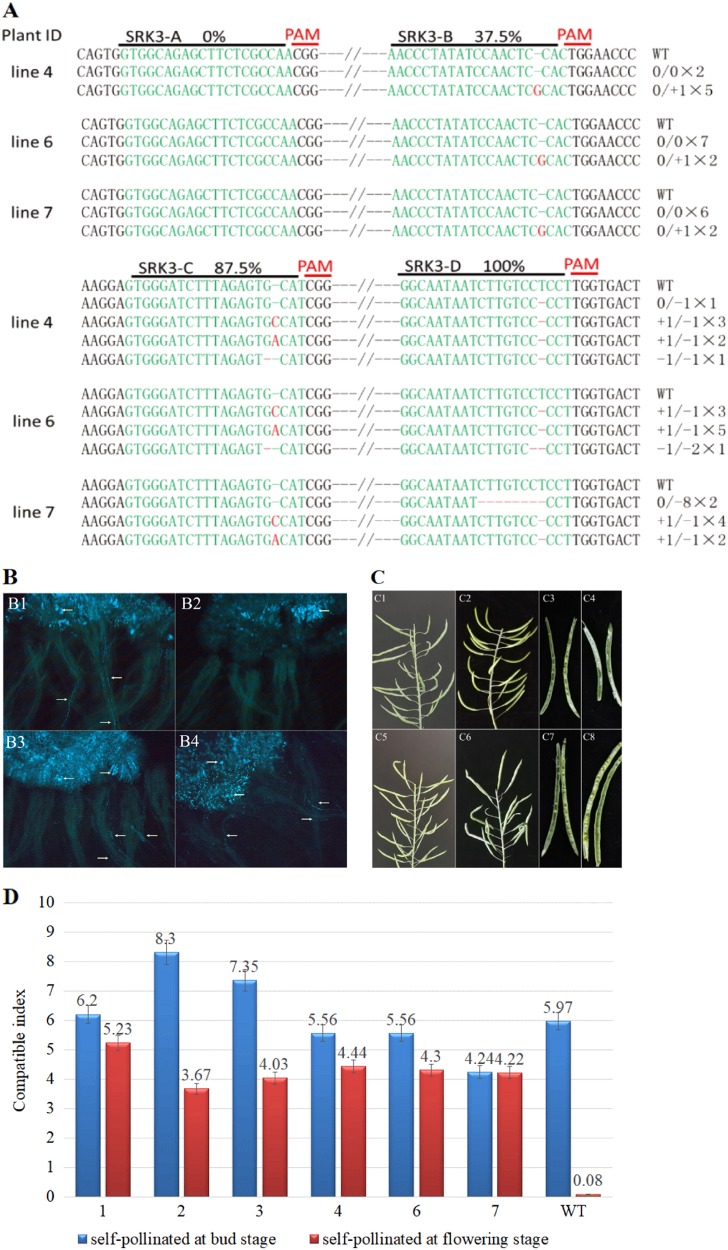
Fig. 3. Targeted mutagenesis of the BoSRK3 gene (X79432.1) by tRNA-processing system-based editing.
a Summary of the mutation types and frequencies in sites A–D. The target sequences are shown in green, and the mutations are shown in red. b In situ fluorescence microscopy of pollen germination on the stigma of the mutant plants and wild-type plants. b1 Bud stage self-pollination of the wild-type plants. b2 Flowering stage self-pollination of the wild-type plants. b3 Bud stage self-pollination of the mutant plants. b4 Flowering stage self-pollination of the mutant plants. White arrows indicate pollen grain germination on the stigma and pollen tube growth down the style. c Silique growth and seed setting in the mutant and wild-type plants. c1 and c3 Silique growth and seed setting of the wild-type plants after the bud stage self-pollination. c2, c4 Silique growth and seed setting of the wild-type plants after flowering stage self-pollination. c5, c7 Silique growth and seed setting of mutant plants after the bud stage self-pollination. c6, c8 Silique growth and seed setting of mutant plants after the flowering stage self-pollination. d Investigation of the self-compatibility index of the mutant and wild-type plants at the bud or flowering stages; self-compatibility index = number of seeds/number of flowers. Bars represent the mean ± standard deviation (SD)