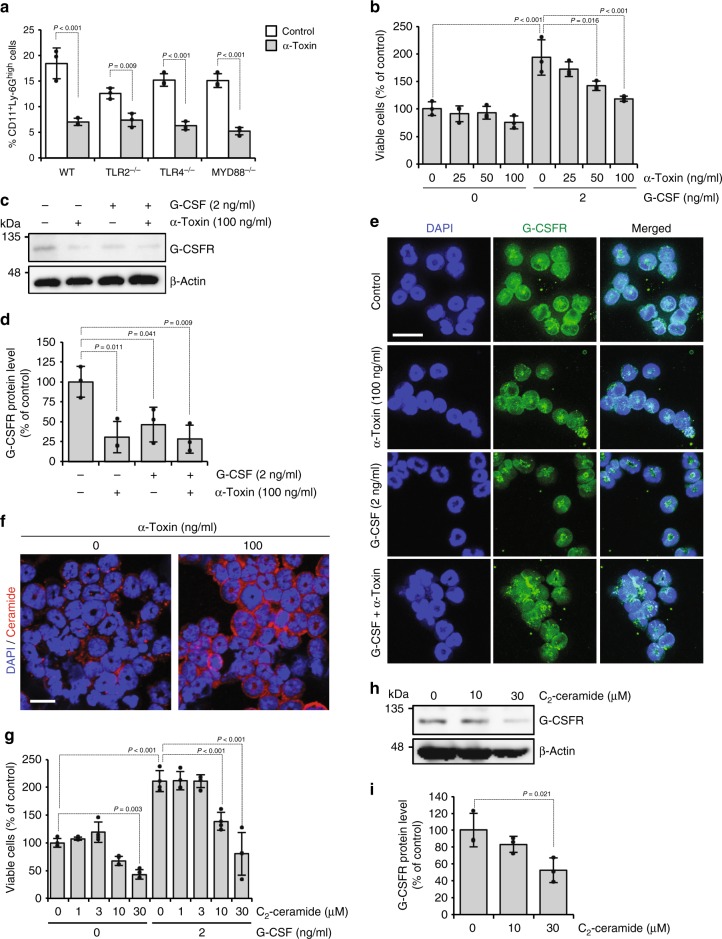
Fig. 4.
α-Toxin makes neutrophils insensitive to granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF). a Bone marrow cells derived from wild-type (WT), Tlr2−/− (TLR2−/−), Tlr4−/− (TLR4−/−), and Myd88−/− (MYD88−/−) mice were cultured for 24 h in the presence or absence (Control) of 100 ng ml−1 α-toxin (α-Toxin), and flow cytometric analysis was performed. The frequency of CD11b+Ly-6Ghigh neutrophils is shown (n = 3 per condition). b–e Magnetically isolated Ly-6G+ cells were cultured for 24 h in the presence or absence of the indicated concentrations of G-CSF and α-toxin. The viable cells were determined using a Cell Counting Kit-8 (b, n = 3 per condition). Whole-cell extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting with specific antibodies against G-CSFR and β-actin, and the density of bands was measured (c, d, n = 3 per condition). Representative blots are shown of three independent experiments, raw gel images are available in Supplementary Figure 9 (c). Localization of G-CSFR was monitored by an immunostaining assay (e). Scale bar, 20 µm. f Ly-6G+ cells were cultured for 30 min in the presence or absence of 100 ng ml−1 α-toxin. The cells were subjected to immunofluorescence analysis of ceramide. Scale bar, 20 µm. g–i Ly-6G+ cells were cultured for 24 h in the presence or absence of the indicated concentrations of G-CSF and C2-ceramide. The viable cells were determined using a Cell Counting Kit-8 (g, n = 4 per condition). Whole-cell extracts were analyzed by immunoblotting with specific antibodies against G-CSFR and β-actin, and the density of bands was measured (h, i, n = 3 per condition). Representative blots are shown of three independent experiments, raw gel images are available in Supplementary Figure 9 (h). One-way analysis of variance was employed to assess statistical significance. Values are mean ± standard deviation. Similar results were obtained in two independent experiments