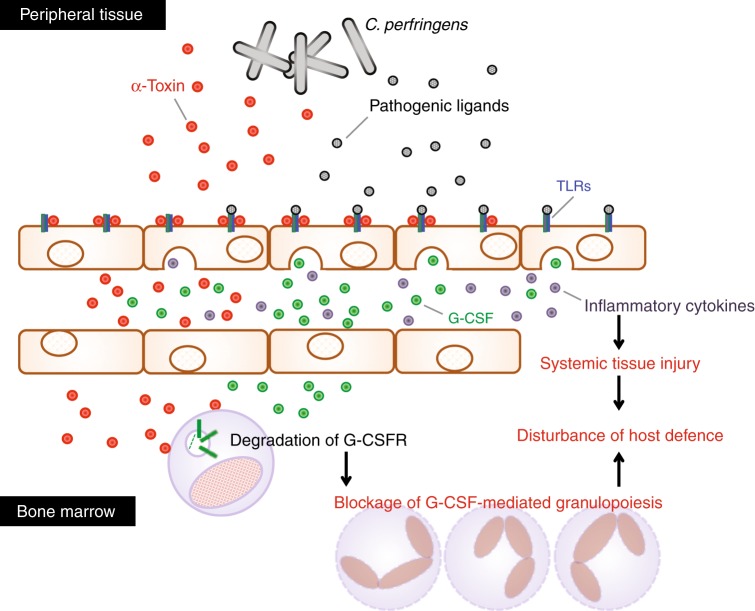
Fig. 6.
Model of disturbed host defense by blockage of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF)-mediated granulopoiesis and Toll-like receptor (TLR)-mediated overproduction of inflammatory cytokines in a C. perfringens-infected host. α-Toxin upregulates the production of G-CSF from endothelial cells by promoting pathogenic ligand-induced TLR signaling, but the toxin makes neutrophils insensitive to G-CSF by inducing the degradation of its receptor, which could be relevant to the α-toxin-mediated blockage of granulopoiesis. Furthermore, α-toxin augmented the TLR-mediated inflammatory response, resulting in systemic and/or local tissue injury through the overproduction of inflammatory cytokines. Thus α-toxin disturbs host defense by modulating G-CSF receptor (G-CSFR)-mediated granulopoiesis and TLR-mediated inflammation