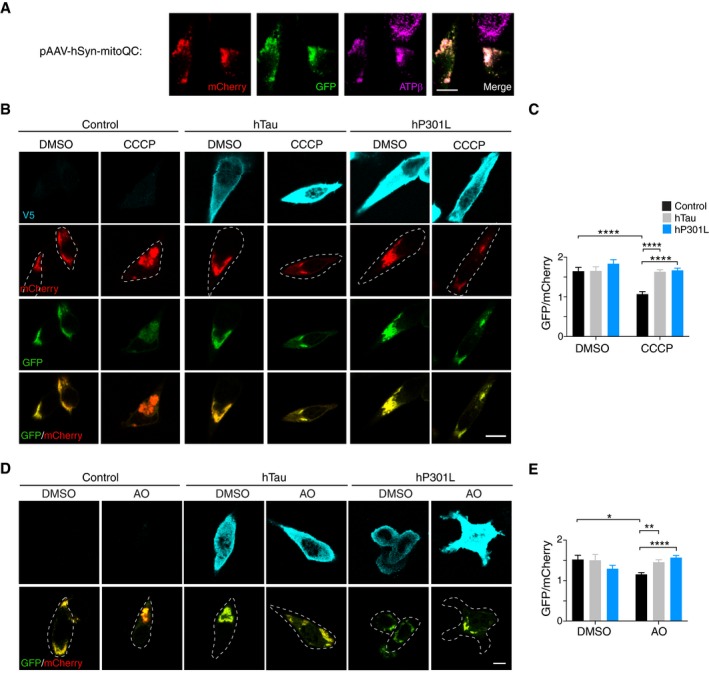
Immunostaining for the mitochondrial marker ATPβ in N2a cells expressing mito‐QC.
N2a cells expressing mito‐QC and myc‐Parkin together with hTau‐V5, hP301L‐V5 or an empty vector control. Treatment with CCCP (8 μM, 17 h) induces mitophagy in control cells, as indicated by a decrease in the GFP/mCherry fluorescence ratio, but not in hTau or hP301L cells. Deconvolution (Classic Maximum Likelihood Estimation) was applied to images for display only.
Quantification of GFP/mCherry fluorescence intensity per cell. Data were analysed by two‐way ANOVA, showing significant main effects of CCCP treatment, F(1, 314) = 15.66, P < 0.0001, and tau expression, F(2, 314) = 12.26, P < 0.0001, and a significant interaction effect, F(2, 314) = 6.137, P = 0.0024, n = 40–73 cells/group.
Cells expressing mito‐QC and myc‐Parkin together with hTau‐V5, hP301L‐V5 or an empty vector control, treated with a mixture of antimycin and oligomycin (AO, 15 μM, 17 h).
Quantification of GFP/mCherry fluorescence intensity per cell. Data were analysed by two‐way ANOVA, showing no significant main effects of AO treatment, F(1, 212) = 0.564, P = 0.4534, or tau expression F(2, 212) = 1.579, P = 0.2087, but a significant interaction effect, F(2, 212) = 9.854, P < 0.0001, n = 16–50 cells/group.
0.0001 for simple effects. Scale bar = 5 μm in (A) and 10 μm in (B, D).