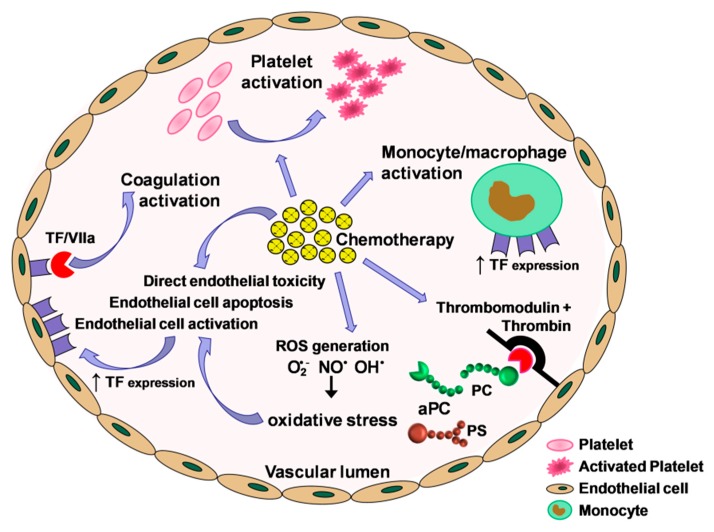
Figure 2.
Effects of chemotherapy on coagulation activation. Chemotherapy may cause incongruous activation of hemostasis through various mechanisms: direct endothelial cell toxicity and apoptosis; vascular cell activation, resulting in tissue factor (TF) exposure; production of reactive oxygen species (ROS); unbalance of factors involved in the control of the coagulation cascade, with an impairment of the protein C (PC)/protein S (PS) anticoagulant pathway; activation of the monocyte/macrophage system and platelets. aPC: activated Protein C; (O2•−): superoxide anion; (OH•): radical hydroxyl radical; (NO•): nitric oxide; TF: tissue factor.