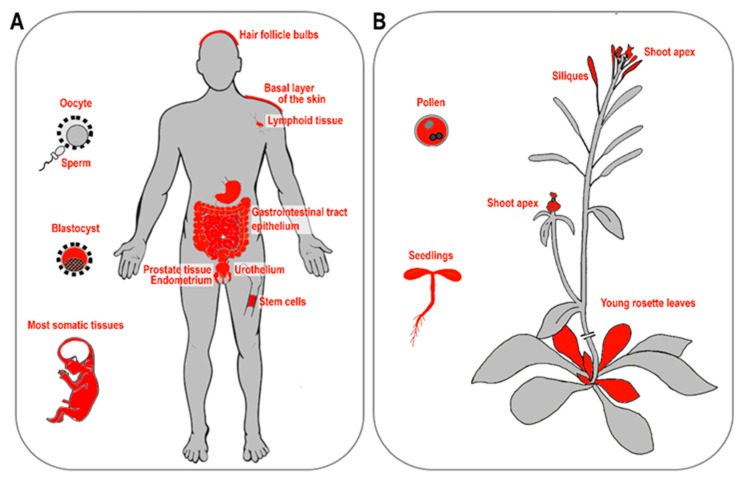
Figure 1.
Telomerase activity in human and plant tissues. (A) During human embryonic development, high telomerase activity is detected in the blastocyst, but not in mature spermatozoa or oocytes. Highly active telomerase is detected in 16 to 20-week-old human fetuses in most somatic tissues with the exception of brain tissue [18,28]. In adults, low telomerase activity is detected in hair follicule bulbs [29], basal cells of crypt and villi or muconasal basal cells of the gastrointestinal tract, basal keratinocytes of the skin [30], lymphocytes, blood bone marrow, and stem cells [31,32,33], and urothelium [34]. High telomerase activity is detected in prostate tissues and endometrium [30,35]. (B) High telomerase activity is detected in plant pollen, seedling, young rosette leaves, and silliques [21,36,37,38,39]. Likewise, both apical meristems—shoot and root—show high telomerase activity [36,37,38]. Figures adopted from human and Arabidopsis eFP browsers [40].