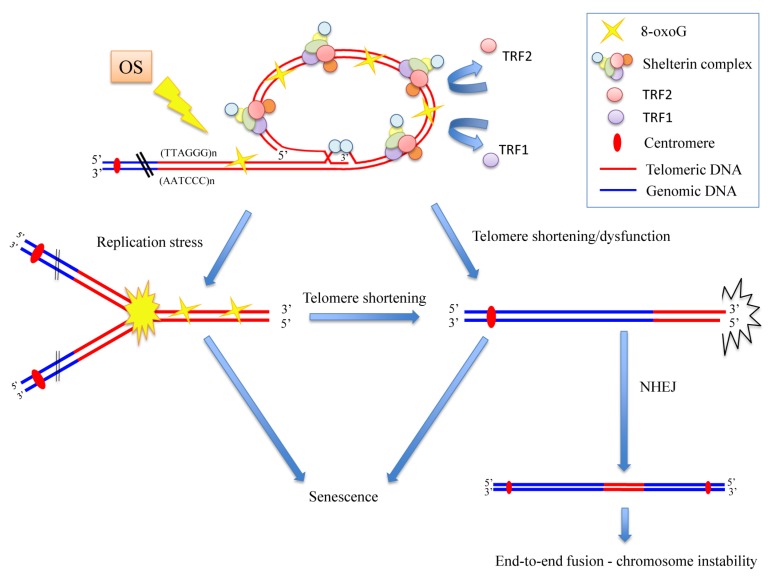
Figure 10.
Model of how oxidative stress (OS) induces chromosome instability mainly by telomere damage. We suppose that 8-oxoG, induced by oxidative stress, is responsible of TRF1 and TRF2 reduction. The decreased binding of these telomeric proteins is responsible of replication fork arrest and telomere shortening/dysfunction that in turn cause senescence and chromosome instability, especially end-to-end fusions. NHEJ (non-homologous end joining).