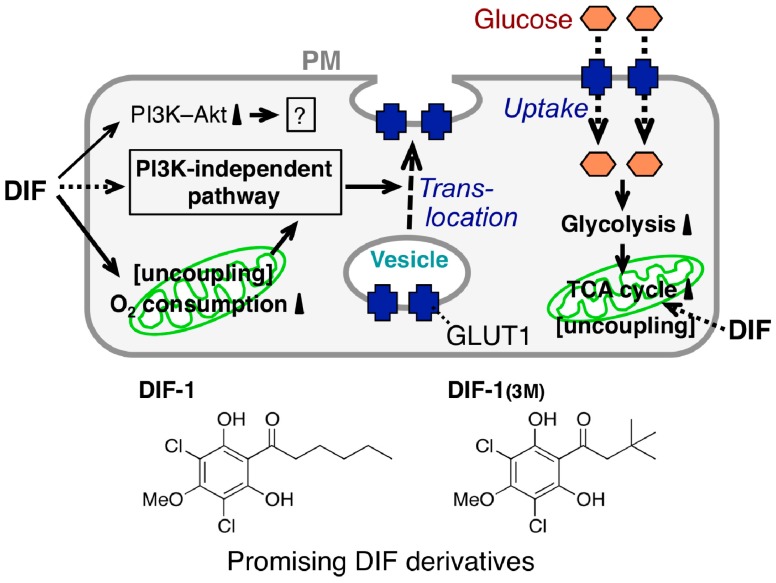
Figure 6.
Proposed scheme for the glucose uptake-promoting effect of DIFs. Stimulation with a DIF induces glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1) translocation from intracellular vesicles to the plasma membrane (PM) via a PI3K–Akt-independent pathway, resulting in the promotion of glucose uptake by confluent mammalian cells [84]; the DIFs activate PI3K and Akt but this is not related to the DIF glucose uptake-promoting activity [84]. The DIFs also function as mitochondrial uncouplers, promoting oxygen consumption [77] and glucose metabolism (glycolysis and subsequent degradation in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle) [85] by mitochondria; this further increases GLUT1 translocation and promotes glucose uptake into the cells. Chemical structure-activity relationship analysis revealed that DIF-1 and DIF-1(3M) are promising lead compounds for the development of anti-diabetes and anti-obesity drugs [71,84,85].