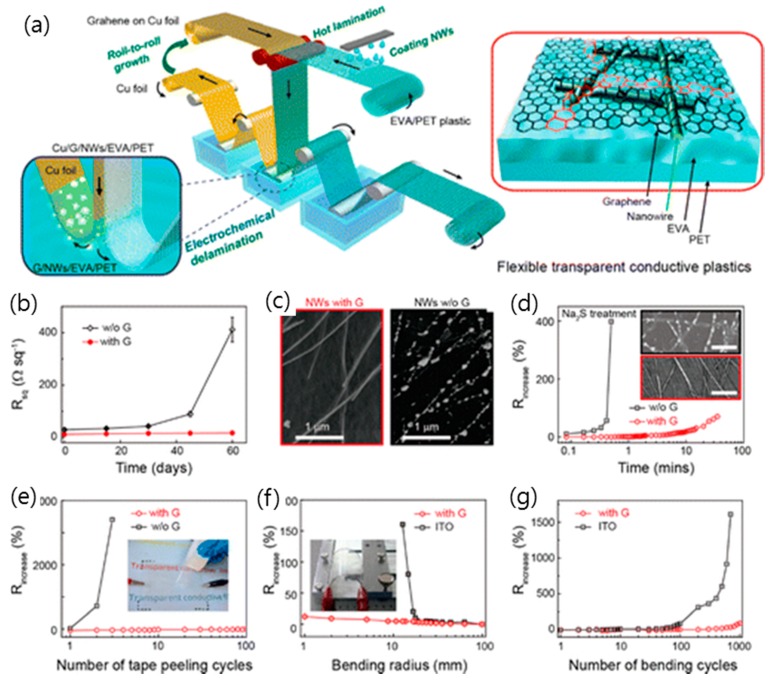
Figure 8.
(a) Schematic and structure of graphene and metal nanowire hybrid films produced by a continuous roll-to-roll process. (b) The durability of graphene and metal nanowire hybrid transparent electrodes. Changes in sheet resistance of pure AgNW films and the graphene/AgNW hybrid films exposed in air at room temperature for 2 months. (c) SEM image of the graphene/AgNW hybrid film and pure AgNW films exposed in air for two months, revealing that AgNWs without the protection of graphene were oxidized to break. (d) Changes in sheet resistance of pure AgNW films and the graphene/AgNW hybrid films under the attack of aqueous Na2S (4 wt.%). (Inset) Morphologies of AgNWs with or without the graphene coverage attacked for 30 s, respectively. Scale bar: 1 μm. (e) Variations in sheet resistance of pure AgNW films and graphene/AgNW hybrid films as a function of the number of cycles of repeated peeling by 3M Scotch tape. (f) Variations in sheet resistance versus bending radius for the hybrid transparent plastic electrodes and ITO films on 150 μm thick PET. (g) Variations in sheet resistance of the hybrid transparent plastic electrodes and ITO films on PET as a function of the number of cycles of repeated bending to a radius of 20 mm. Reproduced with the permission of Reference [54]. Copyright 2015, American Chemical Society.