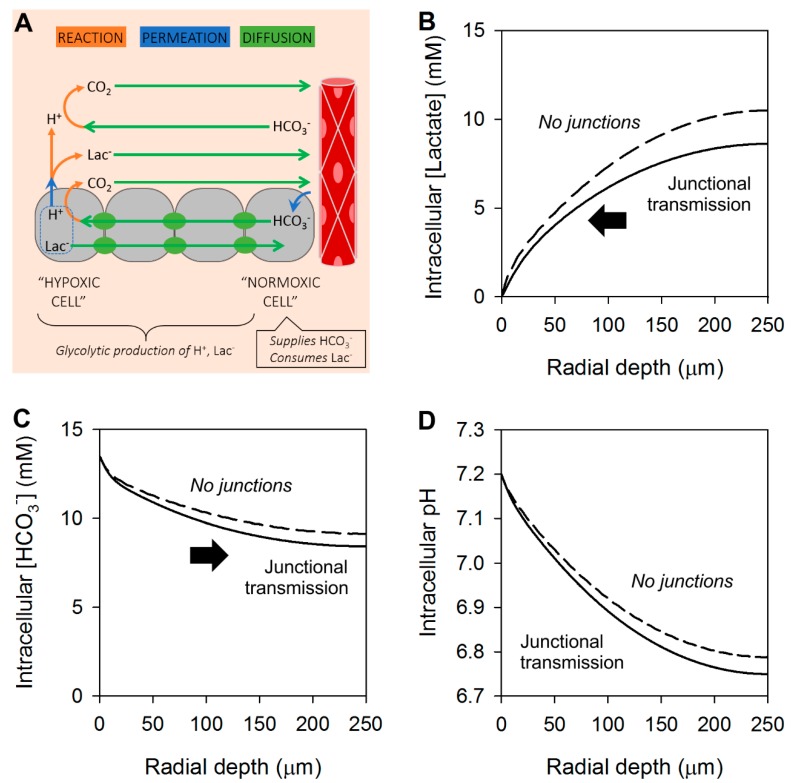
Figure 4.
Modeling the radial distribution of lactate, HCO3− and H+ ions in tissues with junctional coupling for all ionic species. (A) Schematic representation of the 3-D spherical geometry representing a solid tumor with a hypoxic core. Results of modelling shown as radial concentration gradients at the steady-state for (B) lactate, (C) HCO3− and (D) pH in the intracellular space. Arrows indicate direction of diffusive flux. For comparison, dashed lines show results with no junctional coupling, from Figure 2. In this system, intracellular lactate diffuses radially out of the core, leaving behind H+ ions. This generates an inverse gradient of intracellular [HCO3−], which drives a counter-flux of HCO3− i.e., junctional lactate/HCO3− exchange. Overall, lactate venting improves by a fifth.