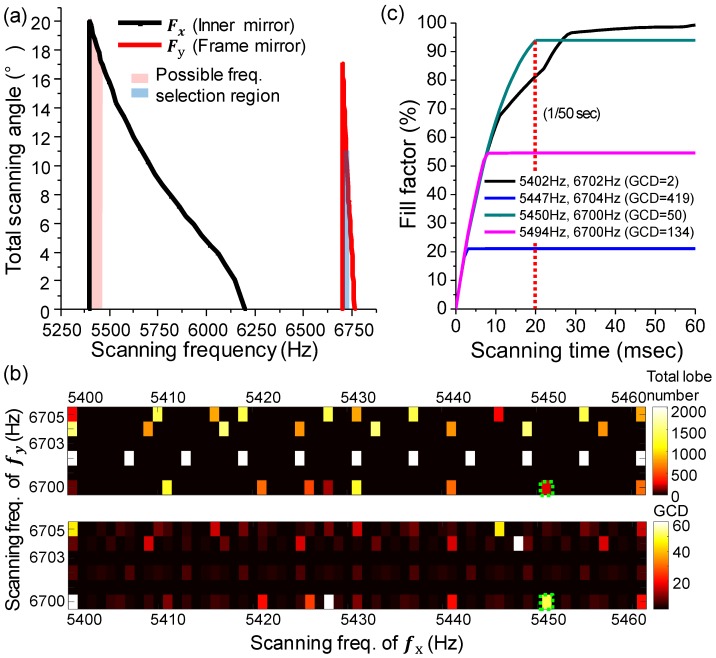
Figure 3.
Scanning properties and scanning frequency selection for HDHF Lissajous scanning. (a) Frequency response of the HDHF Lissajous MEMS mirror. The MEMS mirror has resonant frequencies at 5402 Hz and 6702 Hz in the inner mirror and the frame mirror, respectively. The frequency tuning range should be larger than the greatest common divisor (GCD) frame rate. The inner mirror features a low Q-factor (Q = 18) for frequency selection. (b) Color maps of the GCD and total lobe number for selecting scanning frequency along biaxial frequency domain. High GCD and high total lobe number allow high definition and high frame rate Lissajous scanning. The selected frequency sets for HDHF Lissajous scanning should satisfy the requirements for both a high GCD and high lobe number. For instance, based on the frequency selection rule, the fill factor was over 85% at 256 × 256 pixel resolution, while the total lobe number was 237 or more. Frequency sets where the total lobe number was greater than 237 in the first color map were selected. Next, in the second color map, a frequency set with the higher GCD value was selected from the previously selected frequency set. The scanning frequencies were determined as 5450 Hz and 6700 Hz (GCD = 50, total lobe number = 243) for HDHF Lissajous scanning. HDHF frequency set was selected within the range of 1% of the resonant frequency. (c) Calculated fill factor (FF) of the MEMS mirror along the scanning time. The fill factor initially increased with time; however, the maximum FF and the convergence time varied with the set of selected scanning frequencies. The scanning frequencies of 5450 Hz and 6700 Hz provide a single Lissajous figure of 94% in FF at every 1/50 s.