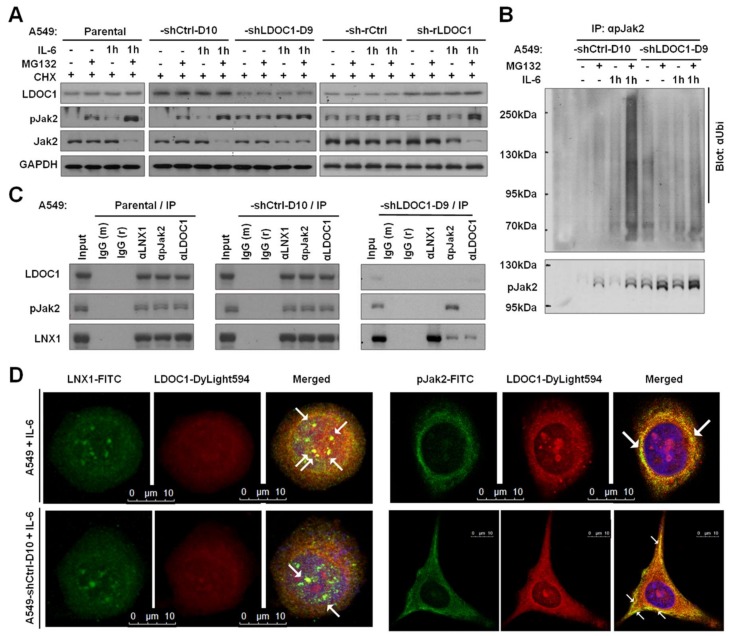
Figure 6.
LDOC1 interacts with Ligand Of Numb-Protein X 1 (LNX1) to promote phospho-JAK2 (pJAK2) degradation through the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway. (A,B) LDOC1 enhances proteasomal degradation (A) and ubiquitination (B) of pJAK2 in basal and IL-6-stimulated A549-derived cell lines. A549-derived cell lines were starved overnight and pretreated with CHX (100 μg/mL), either alone or with proteasome inhibitor MG132 (20 uM) for 3 h before IL-6 (100 ng/mL) stimulation. The cells were lysed in an NP-40 lysis buffer containing MG132 (20 μg/mL) and ubiquitin aldehyde (20 μg/mL) to inhibit isopeptidase activities. (A) Western blotting was performed to examine the levels of indicated proteins. (B,C) The cell extracts were precleared with mouse or rabbit IgG (IgGm or IgGr, respectively) before being immunoprecipitated using antibodies against either pJAK2 (B,C) or against LDOC1 and LNX1 antibodies (C). The input and the Immunoprecipitation (IP) fractions were analyzed through immunoblotting (blot) using antibodies that recognized the indicated proteins. After being stripped, the membrane was reblotted with an anti-pJAK2 antibody (B). (D) Associations between LDOC1-LNX1 and LDOC1-pJAK2 in IL-6-treated A549 and A549-shCtrl-D10 cells. IL-6 stimulated cells were subjected to immunofluorescence assay (IFA) by using anti-LDOC1-DyLight594 (red), anti-LNX1-FITC (green), and anti-pJAK2-FITC (green), respectively. The 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI, blue) was used for nuclear counterstaining. Images were captured using a confocal microscope. IP or IFA performed with IgGm or IgGr were used as negative controls.