Figure 4.
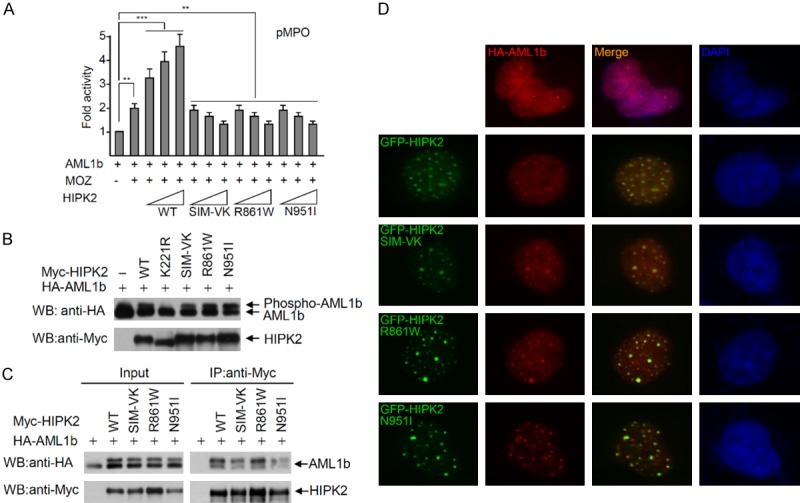
The SIM mutants of HIPK2 do not affect the phosphorylation and interaction with AML1b. A. The HIPK2 R861W and N951I mutants do not activate AML1b-dependent transcriptional activity. The AML1b, MOZ expression plasmid and MPO-reporter plasmid were transfected into 293T cells with increasing amounts of wild-type HIPK2 or a HIPK2 mutant (K221R, SIM-VK, R861W or N951I mutant). Twenty-four hours after transfection, luciferase activities were measured using the Luciferase Assay System (Promega). Transfection efficiency was normalized against β-galactosidase expression. Experiments were repeated at least three times. Error bars indicate the standard error of the means of three independent experiments. The data were statistically analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test (***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01). B. 293T cells were transfected with AML1b and either wild-type HA-HIPK2 or a HIPK2 mutant (catalytically inactive K221R mutant, SIM-VK, R861W or N951I) expression plasmid. AML1b phosphorylation was determined with Western blotting using anti-HA antibody. HIPK2 expression levels were determined by Western blotting using anti-Myc antibody. C. Co-immunoprecipitation of Myc-HIPK2 with AML1b. Either Myc-HIPK2, SIM-VK, R861W or N951I mutant expression plasmid was transfected into 293T cells with the HA-AML1b expression plasmid. Total cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc antibody, followed by Western blotting using anti-HA antibody. D. The SIM mutants of HIPK2 co-localize with AML1b. U2OS cells were transfected with GFP-HIPK2, or various mutants and AML1b. Cells were fixed and immunostained 24 hrs after transfection. Images were obtained with a confocal fluorescent microscope at an excitation wavelength of 488 nm and 543 nm, respectively.
