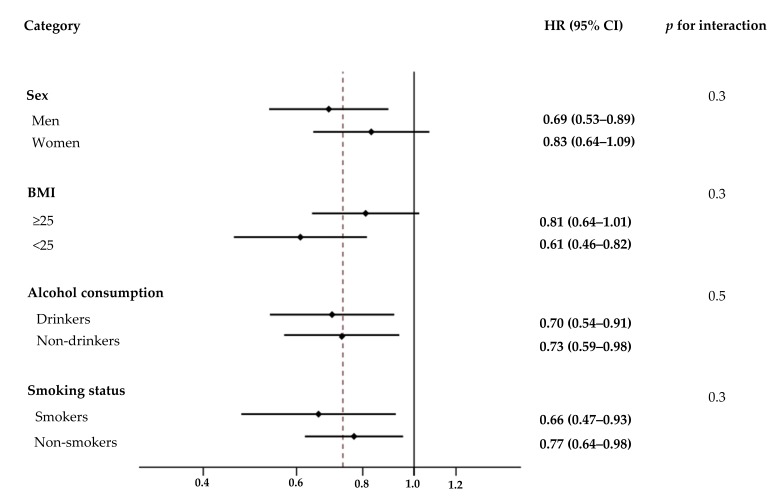
Figure 2.
Effect of various demographic factors on the association between yogurt intake and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs, shown in parentheses) of T2DM in the fourth quartile of energy-adjusted yogurt intake were compared to the first quartile based on sex, body mass index, alcohol consumption, and smoking status. Values were adjusted for the listed variables simultaneously and other potential confounders which included age, residential area, education level, household income, physical activity, history of hypertension, family history of type 2 diabetes, use of antihypertensive medication, use of dietary supplements, and intakes of vegetables, fruits, red meat, processed meat, soft drinks, coffee, and tea. BMI, body mass index.