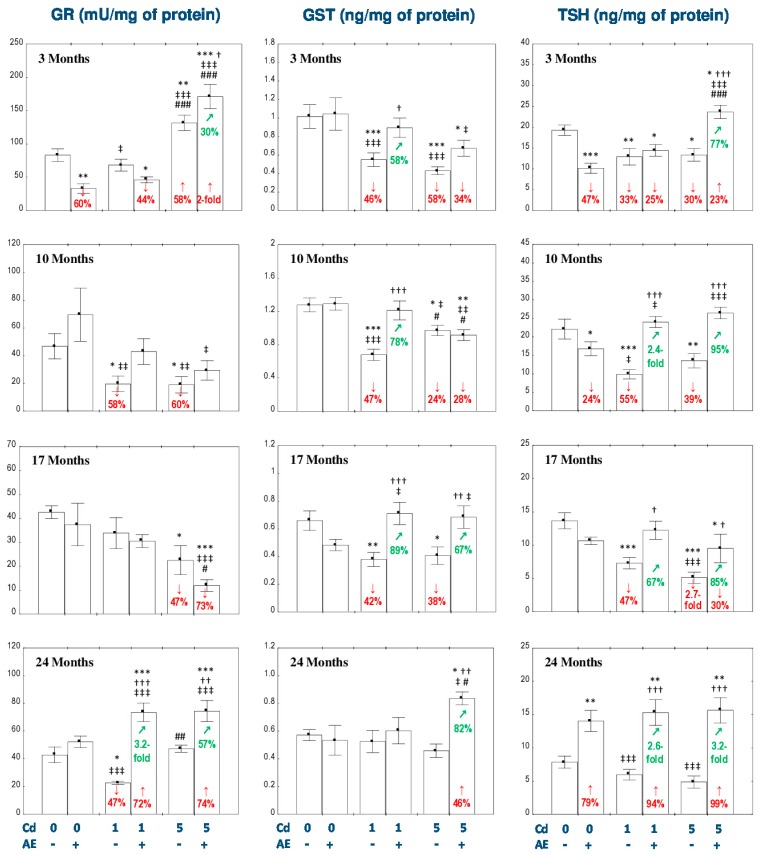
Figure 2.
The effect of the extract from the berries of Aronia melanocarpa L. (AE) on the activity of glutathione reductase (GR) and the concentrations of glutathione S-transferase (GST) and total thiol groups (TSH) in the liver of rats exposed to cadmium (Cd). The rats received Cd in the diet at the concentration of 0, 1, and 5 mg Cd/kg and/or 0.1% aqueous AE (+) or not (-). Data are presented as mean ± SE for eight rats, except for seven animals in the AE, Cd1, and Cd5 group after 24 months. Statistically significant differences (ANOVA, Duncan’s multiple range test): * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 vs. control group; † p < 0.05, †† p < 0.01, ††† p < 0.001 vs. respective group intoxicated with Cd alone; ‡ p < 0.05, ‡‡ p < 0.01, ‡‡‡ p < 0.001 vs. group receiving AE alone; # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001 vs. respective group receiving the 1 mg Cd/kg diet (alone or with AE). Numerical values in bars disclose the percentage changes or factors of changes in comparison to the control group (↓, decrease; ↑, increase) or the respective group receiving Cd alone (↗, increase).