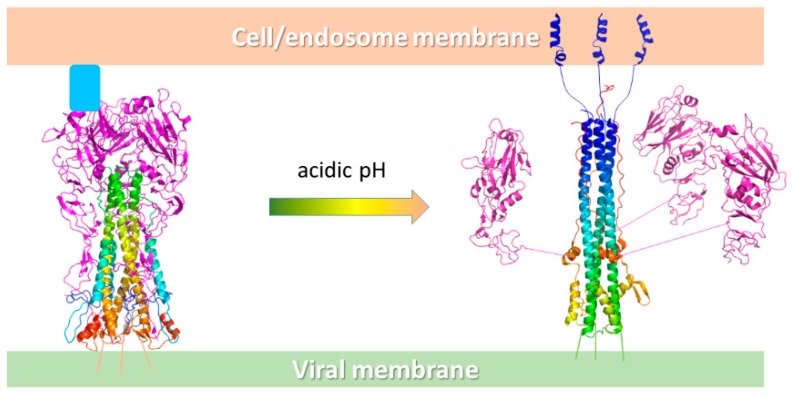
Figure 7.
Schematic representation of the conformational change of HA at acidic pH. On the left, the HA exposed on the viral surface binds the host cell receptor sialic acids (pale blue box) on the HA1 binding sites (purple cartoon), while the HA2 trimer forms the central stem (rainbow cartoon). At acidic pH, the HA2 portion undergoes a relevant conformational rearrangement with the fusion peptide (blue helices) that moves 100 Å away from the original position and inserts into the endosomal membrane. The process ends with the fusion of the viral and host membranes and the release of the viral material into the infected cell.