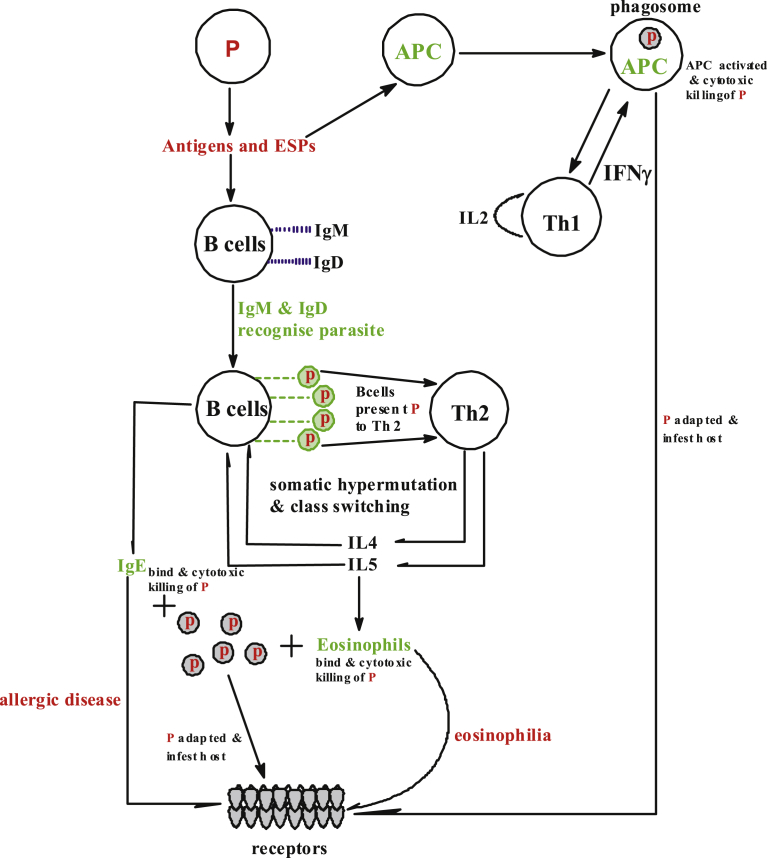
Fig. 2.
Host-parasite interaction; helminths mechanism of survival is by the production of antigens, ESPs and blockage of IL-33R of the host by interacting with alarmins receptors ST2. The innate mechanism of the host response to helminths invasion, firstly by code recognizing parasite using antibodies IgM and IgD from B cells. Then Th2 initiate and stimulate eosinophils and IgE that bind to the helminths causing cytotoxic. The antigens of the parasites are also recognized by antigen presenting cells (APC) which bring about the autonomous response of Th1. In most cases, the parasite survives in the host by immunomodulating the host's immune system. P: helminths parasite, APC: antigen presenting cells, IL: interleukin, IFNγ: Interferon gamma, Ig: immunoglobulin, Th: T-helper.