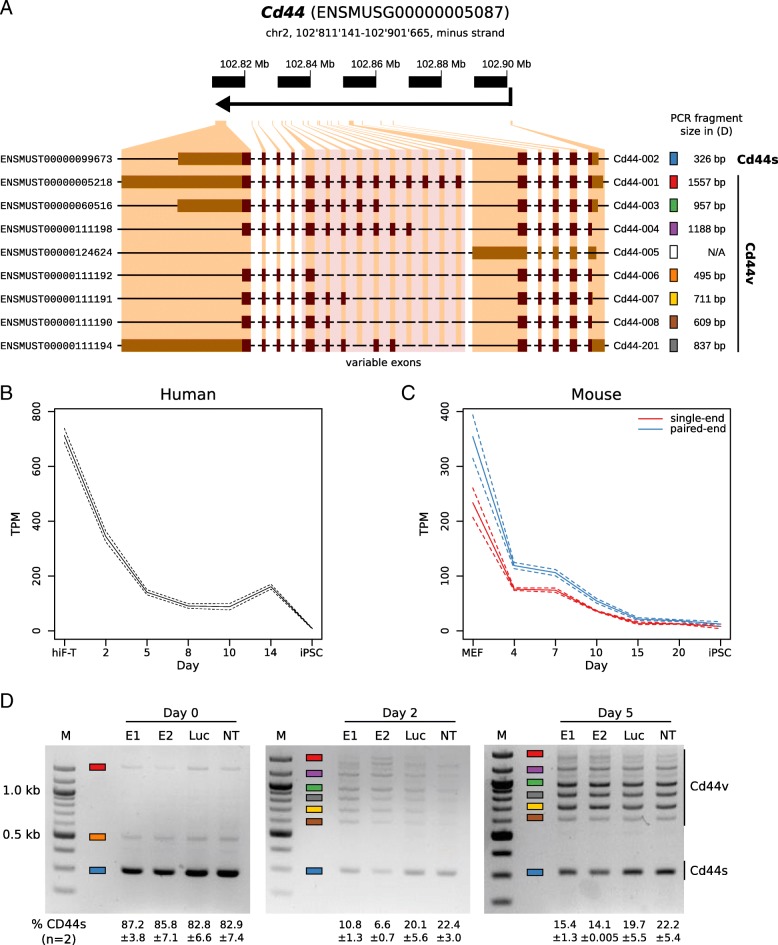
Fig. 4.
ESRPs regulate alternative splicing of CD44. (a) Schematic representation of the murine Cd44 gene model. Indicated are gene coordinates, chromosome ruler, an arrow indicating the direction of transcription, exons, and transcript isoforms with Ensembl identifiers and symbols. Colored boxes and expected PCR fragment sizes were added next to the transcript symbols to facilitate interpretation of (D). The mesenchymal or “standard” (Cd44s) and the epithelial or “variable” (Cd44v) isoforms are highlighted. (b and c) Gene expression profile of the Cd44 gene in human (b; study SRP049340) [28] and mouse (c; study SRP059670) [15] reprogramming time series (x axes). Expression levels (y axes) are given in transcripts per million (TPM). Single- (red) and paired-end (blue) RNA-Seq libraries from study SRP059670 were analyzed separately. Dashed lines indicate 95% confidence intervals. (d) Semi-quantitative RT-PCR of Cd44 isoforms at various time points (days 0, 2 and 5) of TNG-MKOS-MEF reprogramming. Cells ectopically expressed either Esrp1 (E1), Esrp2 (E2), Renilla luciferase (Luc), or no transgene (not transduced, NT). M, 100 bp DNA marker (NEB, #N3231S). The colored boxes represent the different transcript isoforms as defined in (a) Band intensities for the Cd44s isoform, as quantified by AzureSpot (Azure Biosystems), are indicated below the gel photos (n = 2) as in (d). See Additional file 16 for raw quantification data for all bands