Fig. 2. Characterization of crystalline domains in PVA hydrogels.
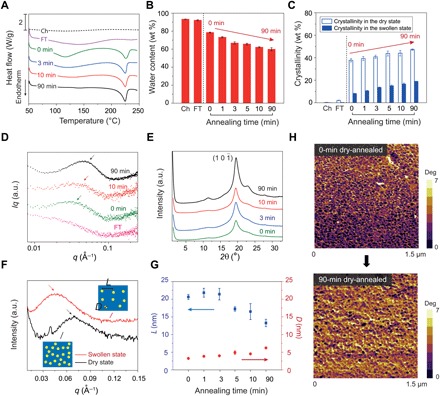
(A) Representative DSC thermographs of chemically cross-linked (Ch), freeze-thawed (FT), and dry-annealed PVA with annealing times of 0, 3, 10, and 90 min. (B) Water contents of chemically cross-linked, freeze-thawed, and dry-annealed PVA with annealing times of 0, 1, 3, 5, 10, and 90 min. (C) Measured crystallinities in the dry and swollen states of chemically cross-linked, freeze-thawed, and dry-annealed PVA with annealing times of 0, 1, 3, 5, 10, and 90 min. (D) Representative SAXS profiles of freeze-thawed and dry-annealed PVA, with annealing times of 0, 10, and 90 min. (E) Representative WAXS profiles of dry-annealed PVA with dry-annealing times of 0, 3, 10, and 90 min. a.u., arbitrary units. (F) SAXS profiles of 90-min dry-annealed PVA in the dry state and swollen state. The insets illustrate the increase of the distance between adjacent crystalline domains due to swelling of amorphous polymer chains. (G) Estimated average distance between adjacent crystalline domains L and average crystalline domain size D of dry-annealed PVA with annealing times of 0, 1, 3, 5, 10, and 90 min. (H) AFM phase images of dry-annealed PVA with annealing times of 0 and 90 min. Data in (B), (C), and (G) are means ± SD, n = 3.
