Fig. 6. SPO16 was required for the stabilization for RPA-SPATA22-MEIOB complex.
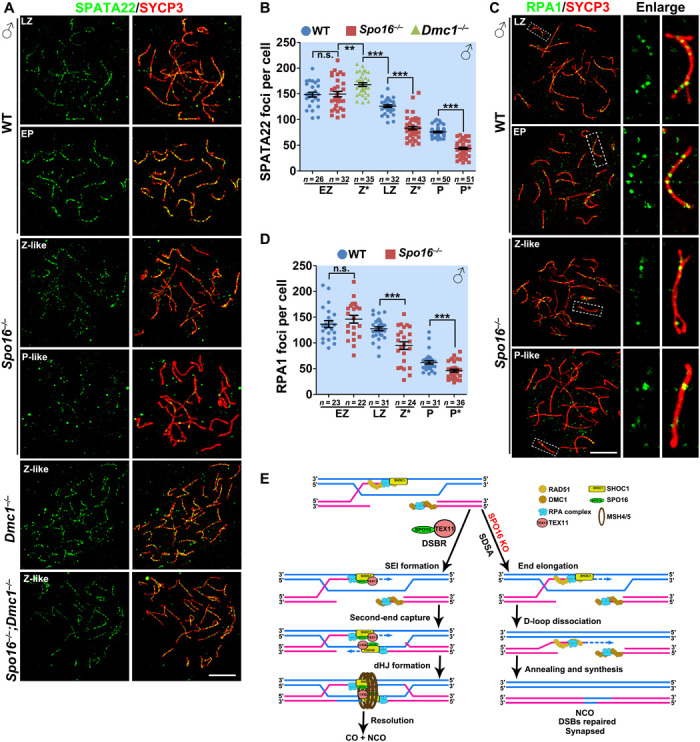
(A and B) SPATA22 was detected on the nuclear surface spreads of WT, Spo16−/−, Dmc1−/−, and Spo16−/−;Dmc1−/− spermatocytes (A), and the quantification is shown in (B). Scale bar, 10 μm. **P < 0. 01 and ***P < 0.001 by two-tailed Student’s t tests. (C and D) RPA1 was detected on the nuclear surface spreads of WT and Spo16−/− spermatocytes (C), and the quantification of RPA1 foci is shown in (D). Scale bar, 10 μm. ***P < 0.001 by two-tailed Student’s t tests. (E) Schematic diagram showing a proposed model of the roles of mammalian SHOC1-SPO16-TEX11 complex in meiotic recombination in meiotic prophase I. After strand invasion, SHOC1 is recruited to the joint molecules or D loops. This is a step crucial for the stabilization of these structures and promoting DNA synthesis and elongation of the DNA ends. After that, SHOC1 further recruits SPO16 and TEX11 to facilitate the repair of DSBs through a DSBR pathway with the formation of dHJs. In the absence of SPO16 or TEX11, the DSBs are repaired via a SDSA pathway. KO, knockout.
