Fig. 4. Detection of P. gingivalis in CSF and oral biofluids from clinical AD subjects.
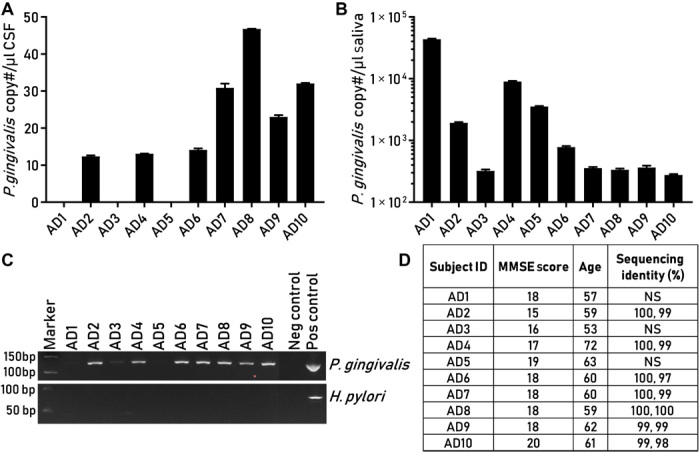
(A) Detection and quantitation of P. gingivalis DNA by qPCR in CSF from subjects with probable AD. (B) Detection and quantitation of P. gingivalis DNA by qPCR from matching saliva samples. (C) Top: PCR products detecting P. gingivalis from CSF in (A) from all subjects run on agarose gel including negative and positive controls containing a synthetic DNA template. Faint or undetectable PCR products from subjects AD1, AD3, and AD5 were below the limit of quantitation for copy number and not of sufficient quantity for sequence analysis. Bottom: qPCR products from CSF from the same subjects for H. pylori. (D) Data table includes age and Mini Mental Status Exam (MMSE) score on subjects and sequence identity of PCR products to P. gingivalis hmuY DNA sequence. Sequence data are included in fig. S4. NS, not sequenced.
