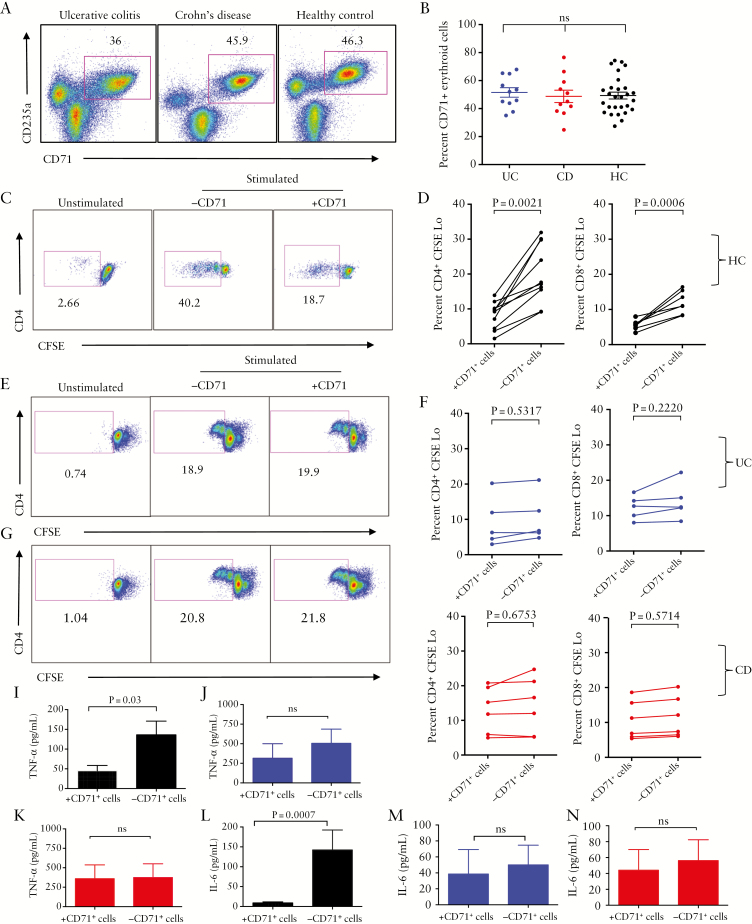
Figure 4.
Impaired functionality of CD71+ erythroid cells from cord blood of newborns to inflammatory bowel disease [IBD] mothers. [A] Representative dot plots showing frequency of CD71+ erythroid cells in cord blood mononuclear cells [CBMCs] of infants born to ulcerative colitis [UC], Crohn’s disease [CD], and healthy control [HC] mothers. [B] Percentages of CD71+ erythroid cells in CBMCs of infants born to UC, CD, and HC mothers. [C] Representative dot plots showing proliferation of CD4+ T cells in the presence or absence of CD71+ erythroid cells among CBMCs of an infant born to an HC mother. [D] Percentages of proliferated CD4+ T cells and CD8+ T cells in the presence or absence of CD71+ erythroid cells among CBMCs of infants born to HC mothers following stimulation with anti-CD3 in vitro. [E] Representative dot plots showing proliferation of CD4+ T cells in the presence or absence of CD71+ erythroid cells among CBMCs of an infant born to a UC mother. [F] Percentages of proliferated CD4+ T cells and CD8+ T cells in the presence or absence of CD71+ erythroid cells among CBMCs of infants born to UC mothers. [G] Representative dot plots showing proliferation of CD4+ T cells in the presence or absence of CD71+ erythroid cells among CBMCs of an infant born to a CD mother. [H] Percentages of proliferated CD4+ T cells and CD8+ T cells in the presence or absence of CD71+ erythroid cells among CBMCs of infants born to CD mothers. [I] TNF-α and [J] IL-6 production by stimulated CBMCs with anti-CD3 antibody obtained from infants born to HC mothers in the presence or absence of CD71+ erythroid cells. [K] TNF-α and [L] IL-6 production by stimulated CBMCs with anti-CD3 antibody obtained from infants born to UC mothers. [M] TNF-α and [N] IL-6 production by stimulated CBMCs with anti-CD3 antibody obtained from infants born to CD mothers in the presence or absence of CD71+ erythroid cells as measured by ELISA.