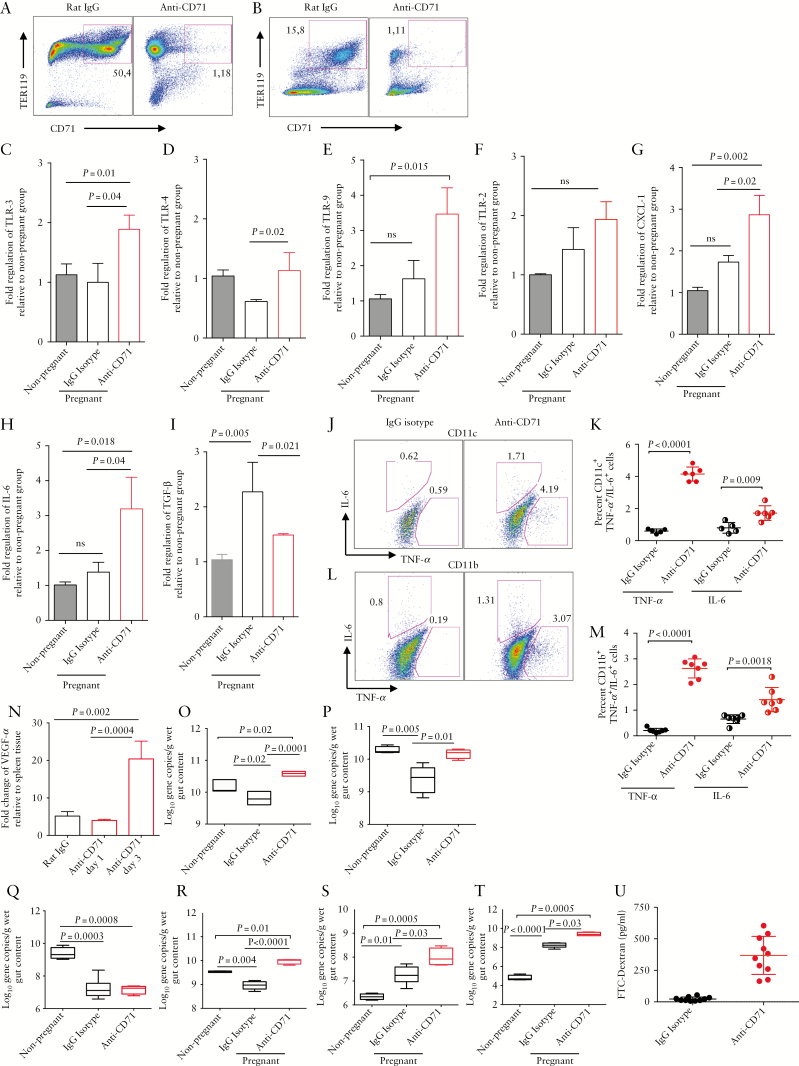
Figure 6.
CD71+ erythroid cells may impact on gut haemostasis during pregnancy. [A] Representative dot plots showing percentages of CD71+ erythroid cells in placenta and [B] spleen of mice before and after anti-CD71 antibody treatment. [C] Expression of TLR-1, [D] TLR-4, [E] TLR-9, [F] TLR-2, [G] CXCL-1, [H] IL-6 and [I] TGF-β genes by gut tissues of non-pregnant compared with pregnant mice treated with rat IgG isotype control or anti-CD71 antibody three days after treatment. [J] Representative plots and [K] cumulative data showing IL-6 and TNF-α production by intestinal CDllc+ cells. [L] Representative plots and [M] cumulative data showing IL-6 and TNF-α production by intestinal CDllb+ cells. [N] Expression of VEGFα gene in placenta tissues. [O] Treated mice were subjected to 16S rRNA-based polymerase chain reaction [PCR] for total bacteria, [P] Bacteroides-Prevotella-Porphyromonas group [Q] Enterobacteriaceae group, [R] Clostridium cluster XIVa, [S] Clostridium cluster 1, and [T] Clostridium cluster IV. [U] Levels of fluorescein isothiocyanate labelled dextran [FITC-dextran] in the blood of IgG versus anti-CD71 treated mice. Data are obtained from a minimum of five mice/group and at least two independent experiments.