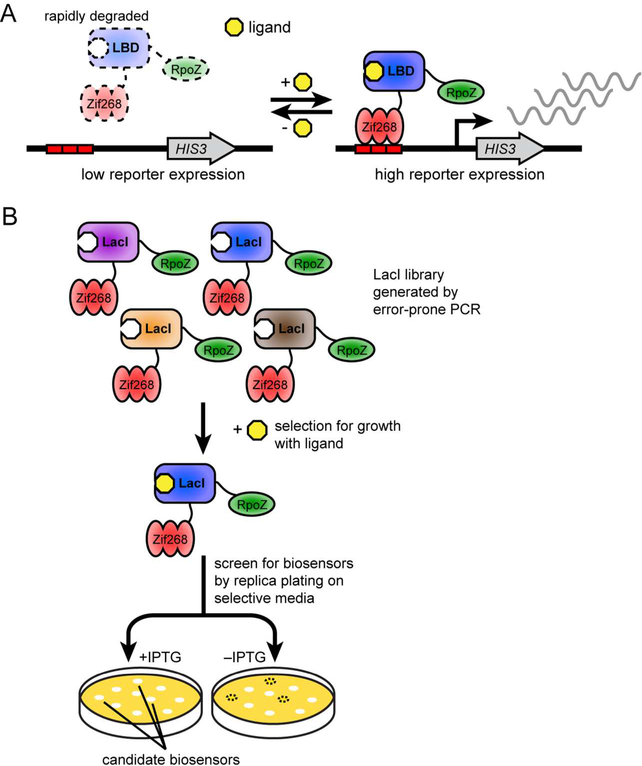
Figure 1.
Design and selection of E. coli biosensors based on ligand-dependent stability. A. A destabilized ligand-binding domain is fused between the Zif268 DNA-binding domain and RpoZ transcription-activating domain. In this biosensor scheme, the absence of ligand would lead to biosensor degradation by natural protein degradation processes, leading to weak transcriptional expression of HIS3. However, in the presence of ligand, binding to ligand would stabilize the biosensor, leading to increased transcriptional expression of HIS3. B. An error-prone PCR library of LacI is fused to Zif268 and RpoZ and subjected to positive selection in minimal media lacking histidine with IPTG ligand. E. coli with biosensor variants that activate expression of HIS3 grow in these selections. Individual biosensors are then screened for ligand-dependence by replica plating their E. coli host on minimal media lacking histidine with and without IPTG.