Table 1.
Typologies of ecosystem services potential.
| Role of the ecosystem | Fate of matter/energy/information | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
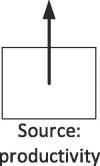 |
Net delivery of biomass or energy eventually leaving the ecosystem | Ecosystems act as sources of matter and energy in the form of biomass. Reference with other classification systems: provisioning services | Generation of mass and biomass |
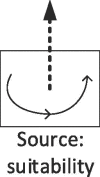 |
Delivery of biomass and energy generated within the ecosystem | Ecosystems act as sources of matter and energy by providing suitable habitats. Reference with other classification systems: regulating services (CICES), supporting services (MA) and habitat services (TEEB) | Habitat maintenance, pollination, pest control and disease control |
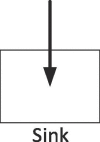 |
Matter or energy absorbed by the ecosystem | Ecosystems act as sinks to store, immobilise or absorb matter. Reference with other classification systems: regulating services (CICES and TEEB) and supporting services (MA) | Absorbing pollutants, carbon, nutrients, heat assimilation |
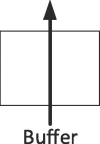 |
Matter or energy flowing through the ecosystem | Ecosystems act as transformers, changing the magnitude of flows of matter or energy. Reference with other classification systems: regulating services | Water retention, flood control |
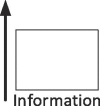 |
Information delivered by the ecosystem | Ecosystems deliver information. The information generated does not modify the original state of the ecosystem. Reference with other classification systems: cultural services | Scenic view, outdoor recreation activities, scientific investigation |
Legend: squares represent an ecosystem unit and arrows represent the type of matter/energy/information delivered.
CICES, Common International Classification of Ecosystem Services; MA, Millennium Ecosystem Assessment; TEEB, The Economics of Ecosystems and Biodiversity.
