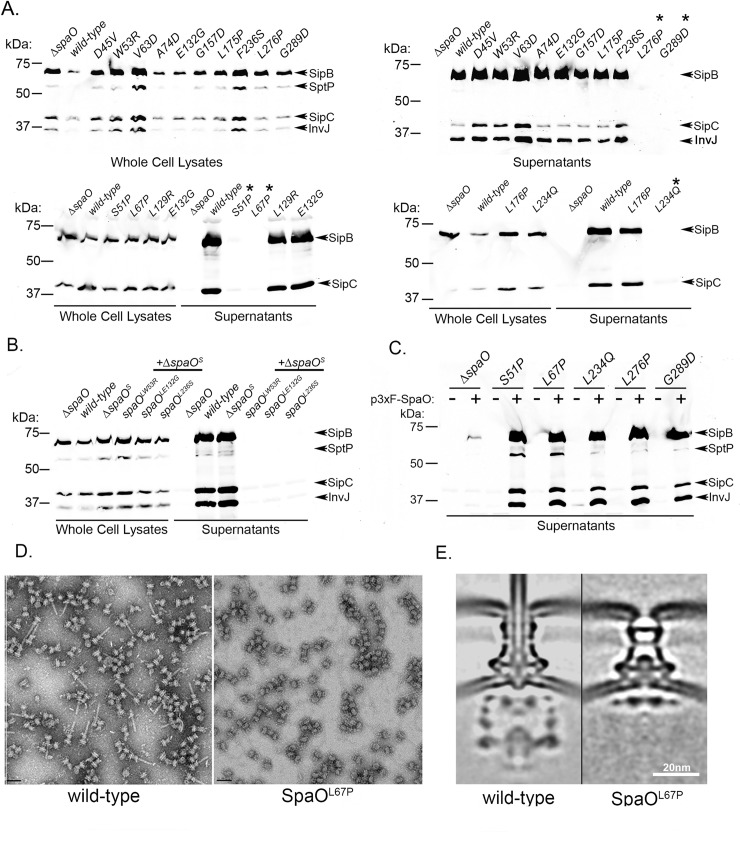
Fig 4. Mutagenesis analysis of SpaOL defines specific functional domains.
(A) Western blots analyzing SipB, SipC, and InvJ secretion in S. typhimurium strains carrying the indicated spaO mutations placed in the chromosome. Eleven out of 16 mutants do not show a phenotype in the presence of SpaOS. Asterisk symbols denote mutants that showed a secretion phenotype. (B) Western blots analysis of SipB, SptP, SipC, and InvJ secretion in S. Typhimurium mutant strains expressing the indicated conditional spaO mutants placed in the chromosome along with a mutation that abolishes the translation of SpaOS. (C) Western blots analysis of the secretion of SipB, SipC, and InvJ in S. Typhimurium strains expressing the indicated spaO mutants complemented in-trans by a wild-type copy of spaO. (D) Electron micrographs of negatively stained needle complexes isolated from wild-type or spaOL67P S. Typhimurium strains show the absence of the needle substructure in the mutant strain. (E) Central sections of the cryo-ET sub-tomogram average of the injectisome structure in wild-type and spaOL67P S. Typhimurium strains showing the absence of sorting platform in the strain expressing the mutant allele.