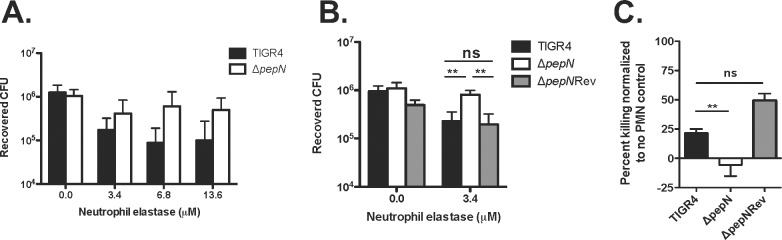
Fig 6. The ΔpepN mutant exhibits enhanced resistance to NE-mediated killing in vitro. and to killing by human neutrophils ex vivo.
A) Approximately 5 x 105 CFU of the TIGR4 or ΔpepN strain were left untreated or exposed to various concentrations of NE. Samples were diluted and plated to enumerate viable CFU. Data presented are the means ± SD from 3–4 independent experiments. P = 0.004 comparing TIGR4 to ΔpepN across all concentrations of NE; P = 0.0035 evaluating dose dependent effect of NE-mediated killing within each individual strain. Statistical analyses were calculated using two-way ANOVA. B) TIGR4, ΔpepN and ΔpepNRev cells were left untreated or were exposed to 3.4μM NE followed by serial dilution and plating to enumerate viable CFU. Data presented are the means ± SD from 3 independent experiments. **, P<0.01; ns = no significant difference. P values were calculated using one-way ANOVA. C) For opsonophagocytic killing experiments, PMNs were isolated from the blood of healthy donors and incubated with pre-opsonized Spn. Viable CFU were determined after serial dilution and plating. The percentage of bacteria killed was determined by comparing surviving CFU for each strain to a no PMN control. Positive percent killing indicates bacterial death while negative percent indicates bacterial growth. Data are shown as the means ± SD from 4 independent experiments with PMNs from four separate donors. P = 0.036 and was calculated using Student’s t-test.