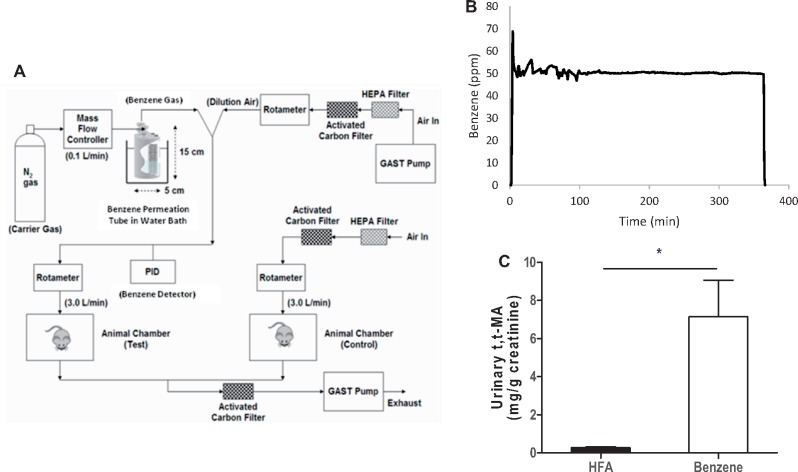
Figure 1.
Benzene inhalation exposures. A, Illustrated is a schematic of the benzene and air exposure system. Benzene was released from a certified permeation tube (Kin-Tek) in a constant temperature water bath into low flow N2 carrier gas (100 ml/min) and diluted to desired level with HEPA-filtered room air (HFA). Benzene concentration (ppm) was monitored continuously with an inline photoionization detector (PID) upstream of the exposure chamber. For control air exposure, HFA was delivered (matched to flow rate as benzene) to a separate, air-only exposure chamber. Exhaust air from benzene and HFA exposure chambers was passed through additional carbon and HEPA filters placed inside a certified fume hood before external exhaust. B, Representative PID data trace of benzene level recorded inline (1 min averages) prior, during and after a 6 h exposure. C, To assess internal exposure, urine collected from mice exposed to either benzene or HFA for 14 days was analyzed for the benzene-specific metabolite, t,t-MA. Shown are the mean t,t-MA levels normalized to creatinine. N = 10 total mice; *p < .05.