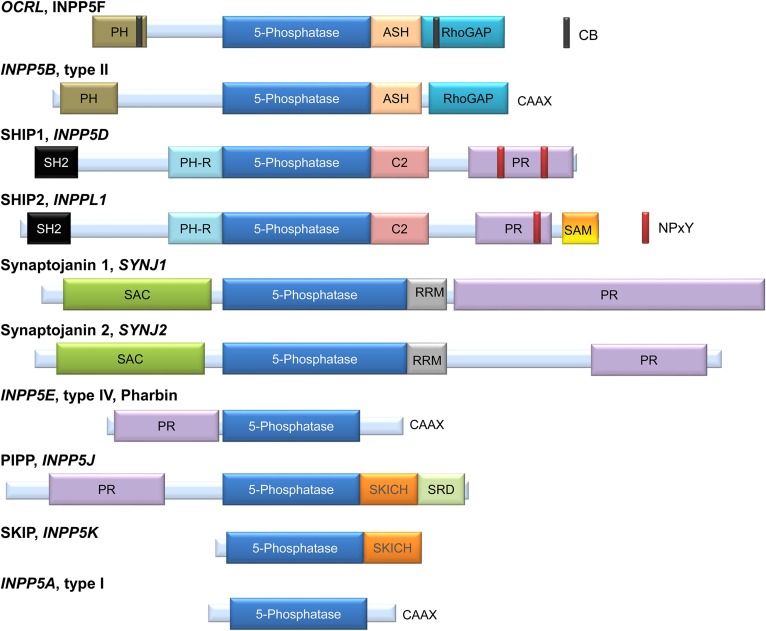
Fig. 1.
Domain and motive organization of the mammalian PI 5-phosphatases. OCRL and INPP5B are very similar in terms of internal domain organization. Both present a PH domain at the N terminus and an ASH domain followed by an RhoGAP domain at the C terminus. OCRL also has two CB domains. INPP5B lacks the CB domains and has a CAAX domain at the C terminus (57, 88–90). SHIP1 and SHIP2 are also very similar in terms of organization; both contain an SH2 domain at the N terminus; a PH-R domain and C2 domain, upstream and downstream of the 5-phosphatase domain, respectively; and a PR domain with two NPxY sequence motifs for SHIP1 and one for SHIP2. SHIP2 also has a SAM domain in the C terminus, but this SAM domain is absent in SHIP1 (91, 92). The SHIP2 ubiquitin-interacting motif at amino acids 1117–1134 has also been reported for SHIP2 (17). SYNJ1 and SYNJ2 show the presence of a SAC at the N terminus, an RRM domain next to the PI 5-phosphatase domain; and a PR domain at the C terminus (93). INPP5E or pharbin is composed of a PR domain at the N terminus and a CAAX sequence at the C terminus (94). PIPP and SKIP have in a common a SKICH domain downstream of the 5-phosphatase domain. PIPP also has a PR domain at the N terminus and an SRD at the C terminus (95, 96). INPP5A or type I 5-phosphatase is the smallest from the family and is constituted, in addition to the 5-phosphatase domain, by a CAAX sequence at the C terminus (6). Figure is adapted from (1, 62). ASH, ASPM-SPD2-hydin; CB, clathrin binding; PH-R, PH-related; PIPP, proline-rich inositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase; PR, proline-rich; RhoGAP, Rho GTPase-activating protein; RRM, RNA recognition motif; SAC, SAC1-like phosphatase domain; SH2, Src homology 2; SKICH, SKIP COOH terminal homology; SRD, serine-rich domain.