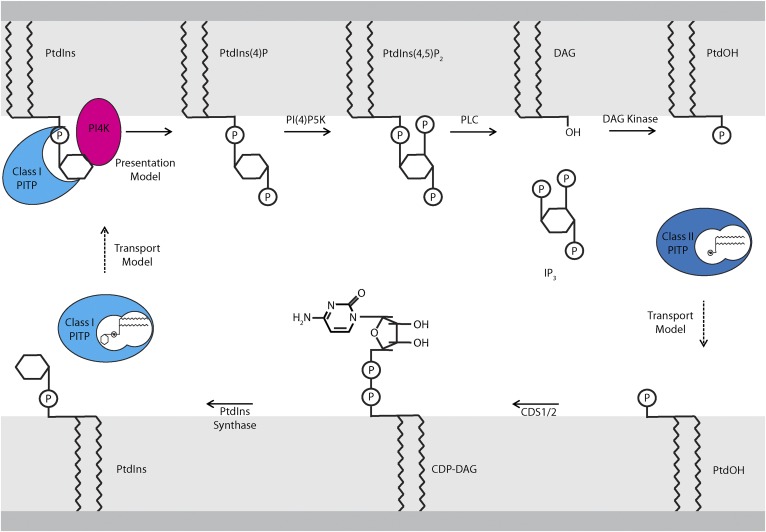
Fig. 2.
Models of PITP function in the PIP cycle. PtdIns is synthesized at the ER by the sequential action of the enzymes, CDS1/2 and PtdIns synthase, which convert PtdOH to CDP-DAG and CDP-DAG to PtdIns, respectively. “Transport models” for describing PITP function postulate that class I PITPs transfer PtdIns from the ER to signaling membranes (i.e., the plasma membrane). “Presentation models” describe PITPs as noncatalytic factors that present PtdIns to PI4K, thereby directly stimulating PtdIns4P synthesis. In the presentation model, PITP utilizes PtdIns at the signaling membrane and does not catalyze PtdIns transport from the ER. PtdIns4P synthesized at the plasma membrane can be converted to PtdIns(4,5)P2, which is then hydrolyzed by agonist-stimulated PLC activity to produce DAG and IP3. DAG is converted to PtdOH by DAG kinase. PtdOH must then be replenished at the ER to restore the PtdIns biosynthetic cycle. Class II PITPs, which bind PtdOH, are proposed to fulfill this role in a transport mechanism.