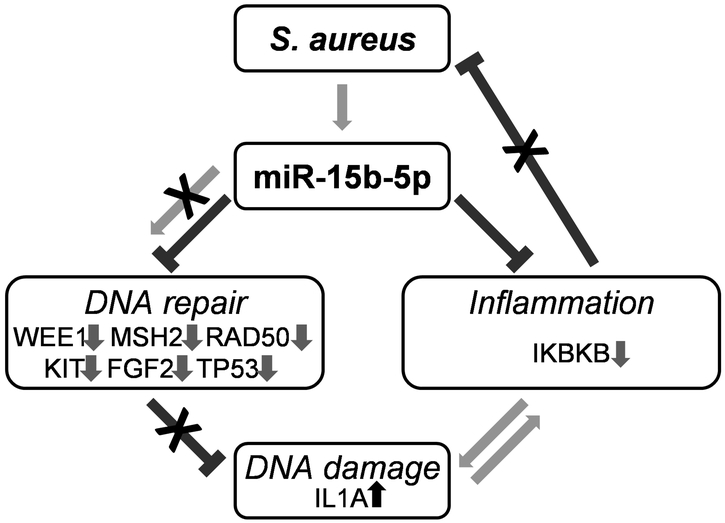
Figure. 5. Diagram summarizing how miR-15b-5p orchestrates processes involved in pathophysiology of DFUs.
Persistent S. aureus colonization in DFUs leads to over-expression of miR-15b-5p resulting in increased DNA damage through suppression of WEE1 and chronic sub-optimal inflammation by targeting IKBKB. DNA repair mechanisms are further inhibited by down-regulation of multiple genes in DFUs including MSH2, RAD50, KIT, FGF2 and TP53. DNA damage feeds into a positive feedback loop by causing the release of IL-1A.