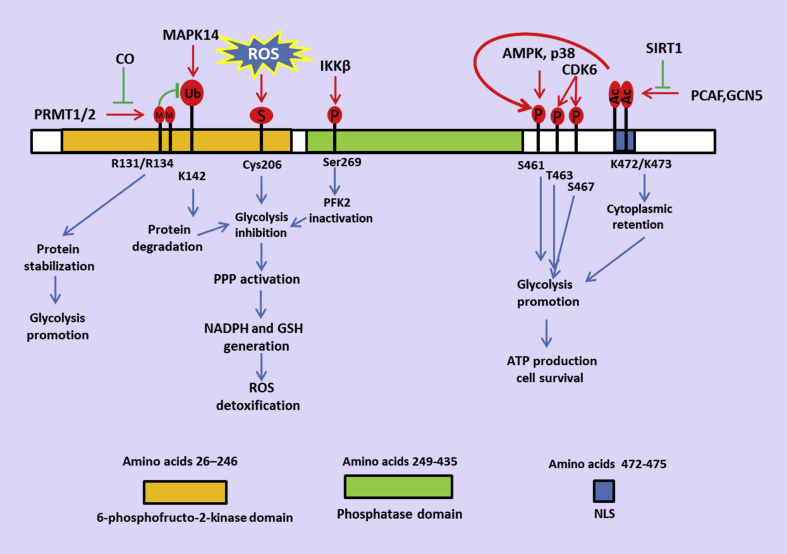
Figure 2.
Multiple post-translational modifications of PFKFB3 differentially regulate glucose utilization. PFKFB3 protein levels, subcellular localization, and PFK2 activity are largely affected by post-translational modifications. Phosphorylation of Ser461 by AMPK and Thr463 and Ser467 by CDK6 activates PFK2 activity and promotes glycolysis. PCAF- and GCN5-mediated acetylation of Lys472/473 disrupts the NLS and sequesters PFKFB3 in the cytoplasm, facilitating its phosphorylation on Ser461 by AMPK. Polyubiquitination on Lys142 of PFKFB3 leads to proteasomal degradation of PFKFB3, shunting glucose metabolism from glycolysis to the PPP. Asymmetrical dimethylation on Arg131 and Arg134 stabilizes PFKFB3. Reduced methylation of PFKFB3 reroutes flux into the oxidative arm of PPP.