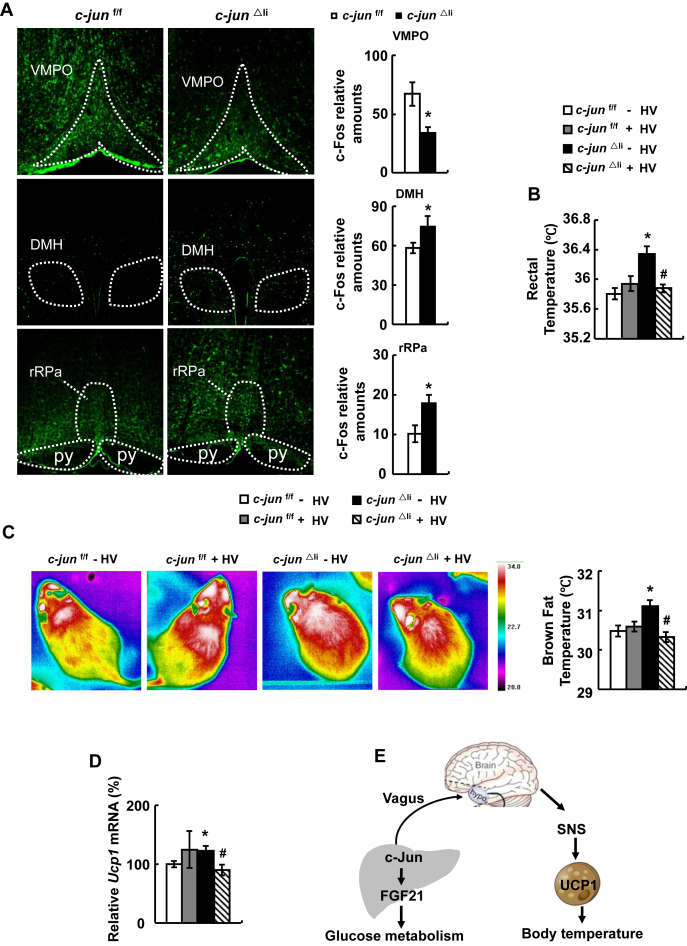
Figure 6.
Selective hepatic vagotomy reverses body temperature in c-jun△limice. (A) Immunofluorescence staining detection of c-Fos protein in the VMPO (top), DMH (middle), rRPa (bottom) and the number of c-Fos positive nuclei in these sections. (B–D) c-jun△li mice or control mice were subjected to selective hepatic vagotomy (+HV) or sham surgery (- HV), then rectal temperature (B), infrared images (C), and UCP1 expression (D) were detected after 7 days. (E) Working model. Data were obtained with mice indicated (n = 5–10 mice per group, 10–12 weeks old) and presented as means ± SEMs. Statistical significance was calculated using two-tailed student t-test for the effects of c-jun△li mice versus the control group (*: p < 0.05) in A, or using one-way ANOVA followed by the Student-Newman-Keuls (SNK) test in B-D (*: p < 0.05 for the effects of any group of mice versus control mice without HV; #: p < 0.05 for the effects of HV versus sham surgery in c-jun△li mice).