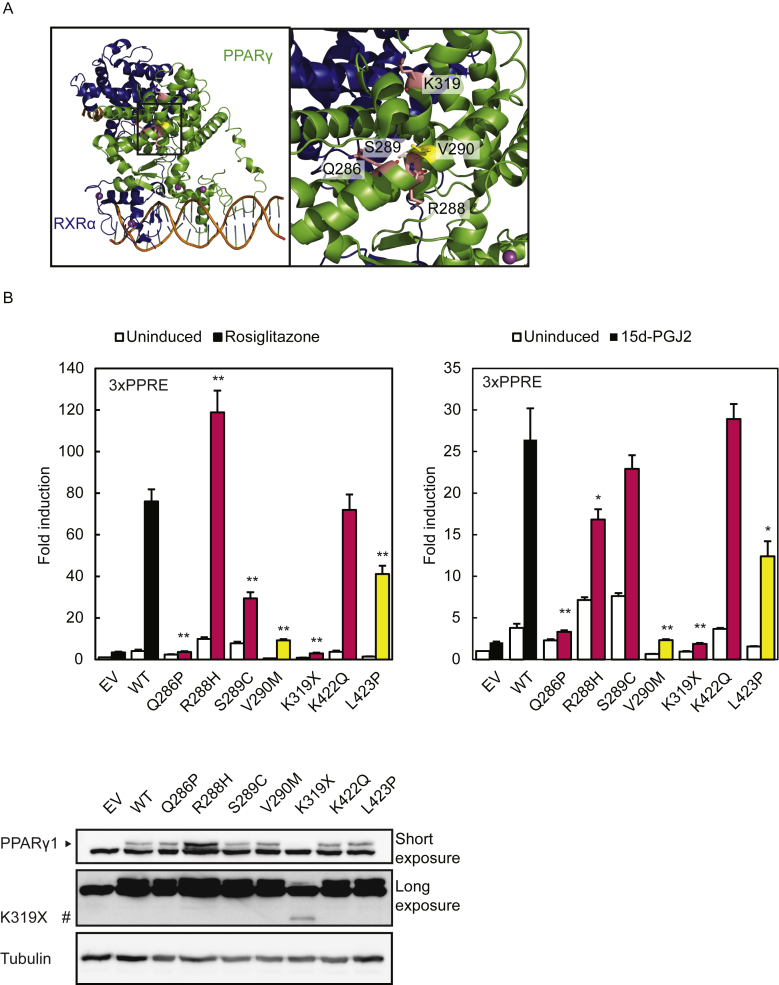
Figure 6.
Colon cancer-associated PPARγ mutants display variable phenotypes. A. Crystal structure of an intact PPARγ–RXRα complex (PPARγ in green; RXRα in blue) bound to DNA (left panel). The square box indicates the magnified region shown in the right panel. In pink, PPARγ Q286, R288, and S289 in helix 3 and K319. Substitution of these residues is associated with colon carcinoma. PPARγ V290, in helix 3, indicated in yellow has previously been described in FPLD3. Protein Database entry 3DZY. The figures were generated by open source software PyMOL 099rc6 (www.pymol.org). B. U2OS cells were transiently cotransfected with expression vectors encoding PPARγ1 WT or PPARγ1 mutants respectively, and 3× peroxisome proliferator response element (PPRE)-Tk-Luc reporter. Activation of the luciferase reporter, in the absence or presence of 1 μM rosiglitazone (left) or 15d-PGJ2 (right), is expressed as fold induction over that with empty vector (EV). Results are averages of at least three independent experiments assayed in duplicate ± SEM. **P < 0.01 cells transfected with mutant vs. WT. Expression levels of the different proteins were confirmed by western blot analysis using a PPARγ specific antibody. WT, wildtype. #, indicates PPARγ1 K319X.