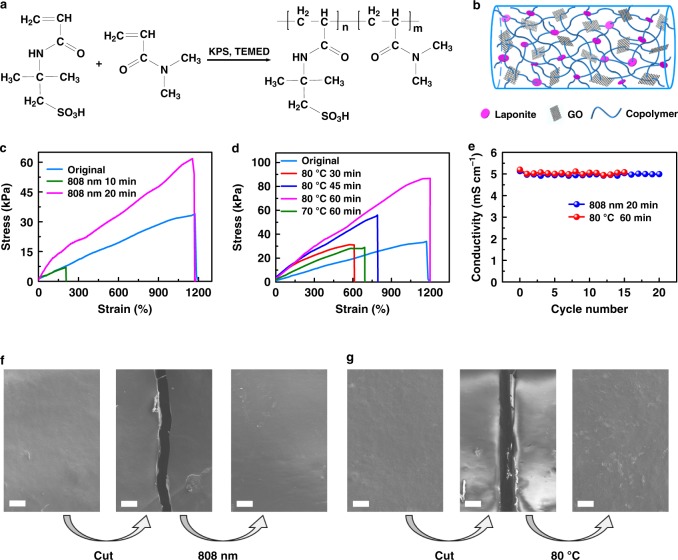
Fig. 1.
Synthesis and properties of the nanocomposite hydrogels. a Schematic of copolymerization of poly(AMPS-co-DMAAm) with potassium persulfate (KPS) and N,N,N’,N’-tetramethylethylenediamine (TEMED) served as initiator and catalyst, respectively. b Schematic of poly(AMPS-co-DMAAm)/Laponite/graphene oxide (GO) nanocomposite hydrogels with Laponite and GO served as cross-linkers. c, d Healable property of hydrogels under irradiation of 808 nm infrared light for 20 min (c) and heating treatment at different temperature (d). e Electrical conductivity retention of a hydrogel film after cyclic broken/healed process. f, g Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of poly(AMPS-co-DMAAm)/Laponite/GO hydrogels being healed by treatment of 808 nm infrared light irradiation for 20 min (f) and 80 oC for 60 min (g). The scale bar: 100 μm