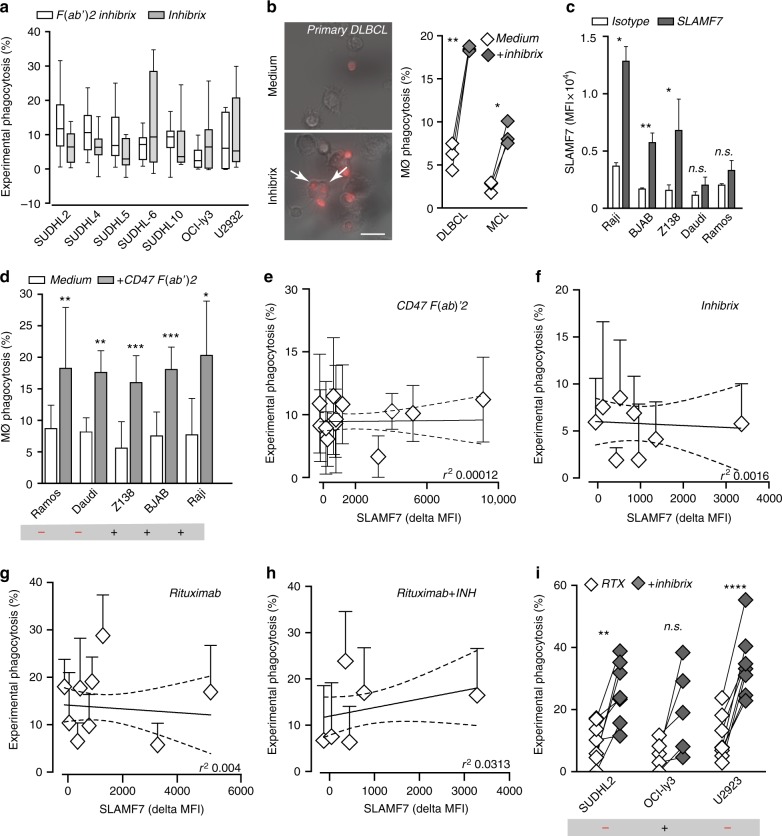
Fig. 3.
Efficacy of CD47-targeting antibodies in B-cell malignant cells does not correlate with SLAMF7 expression. a Experimental phagocytosis of DLBCL lines by macrophages either upon CD47 F(ab′)2 treatment or inhibrix treatment (n = 3). Box plot contains center line representing median and whiskers representing 5–95%. b Representative microscopy pictures of phagocytosis of primary DLBCL cells by autologous macrophages upon 3 h treatment with inhibrix. Quantification of phagocytosis of primary DLBCL and MCL cells by autologous macrophages. c Quantification of surface SLAMF7 expression on five NHL lines (n = 3). d Percentage of phagocytosis of NHL cell lines by allogeneic human macrophages primed with LPS/IFN-γ upon 3 h treatment with F(ab′)2 of anti-CD47 antibody inhibrix (CD47 F(ab′)2) vs. untreated cells (n = 3–4). e Correlation between SLAMF7 expression and the percentage of experimental phagocytosis induced by CD47 F(ab′)2 in NHL and DLBCL cell panel (n = 3). f Correlation between SLAMF7 expression and the percentage of experimental phagocytosis induced by anti-CD47 antibody inhibrix in DLBCL cell panel (n = 3–4). g Correlation between SLAMF7 expression and the percentage of experimental phagocytosis induced by Rituximab in NHL and DLBCL cell panel (n = 3). h Correlation between SLAMF7 expression and the percentage of experimental phagocytosis induced by the combinatory treatment of Rituximab and Inhibrix in DLBCL cell panel (n = 3). i Experimental phagocytosis of tumor cells by macrophages upon RTX treatment or combination treatment with inhibrix (n = 3). Experiments with primary patient-derived samples were performed in triplicates. Statistics was performed using paired Student’s t-test. n.s. = not significant, *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001. Error bars stand for standard deviation (SD)