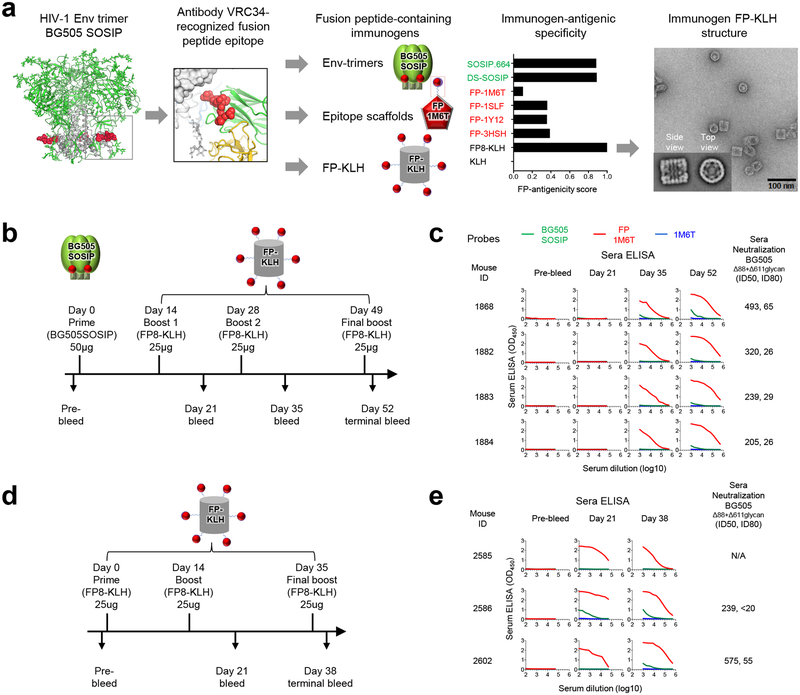
Figure 1.
Design, properties, and immunogenicity of FP immunogens based on the epitope of antibody VRC34.01. (a) Structure-based design, antigenic characteristics, and EM structure of FP immunogens. The glycosylated structure of the HIV-1 Env trimer is shown at far left, with exposed N-terminus of FP highlighted in red. Subsequent images show site recognized by VRC34.01 antibody, schematics and antigenicity of FP immunogens, and negative stain EM of FP-KLH (see Supplementary Fig. 1 for details of FP antigenicity). For EM study, n=3 experiments were performed independent with similar results. (b) Immunization regimen 1. At day 52, mouse spleens were harvested and hybridomas created. (c) ELISA and neutralization of serum from regimen 1-immunized mice. Protein probes used for ELISA are defined in top row and include BG505 SOSIP.664 (green), FP-epitope scaffold based on PDB 1M6T (red), and 1M6T scaffold with no FP (blue). Column 1 defines mouse identification number and subsequent columns show ELISA and neutralization. ELISAs are shown as a function of serum dilution for pre-bleed, days 21, 35, and 52 (ELISA curves colored according to probe, with sera mostly unreactive with IM6T scaffold with no FP). Neutralization (ID50, ID80) values provided for day 52 serum; see Supplementary Fig. 2a for neutralization details. (d) Immunization regimen 2. At day 38, mouse spleens were harvested and hybridomas created. (e) ELISA and serum neutralization of serum from regimen 2-immunized mice, displayed as in c.