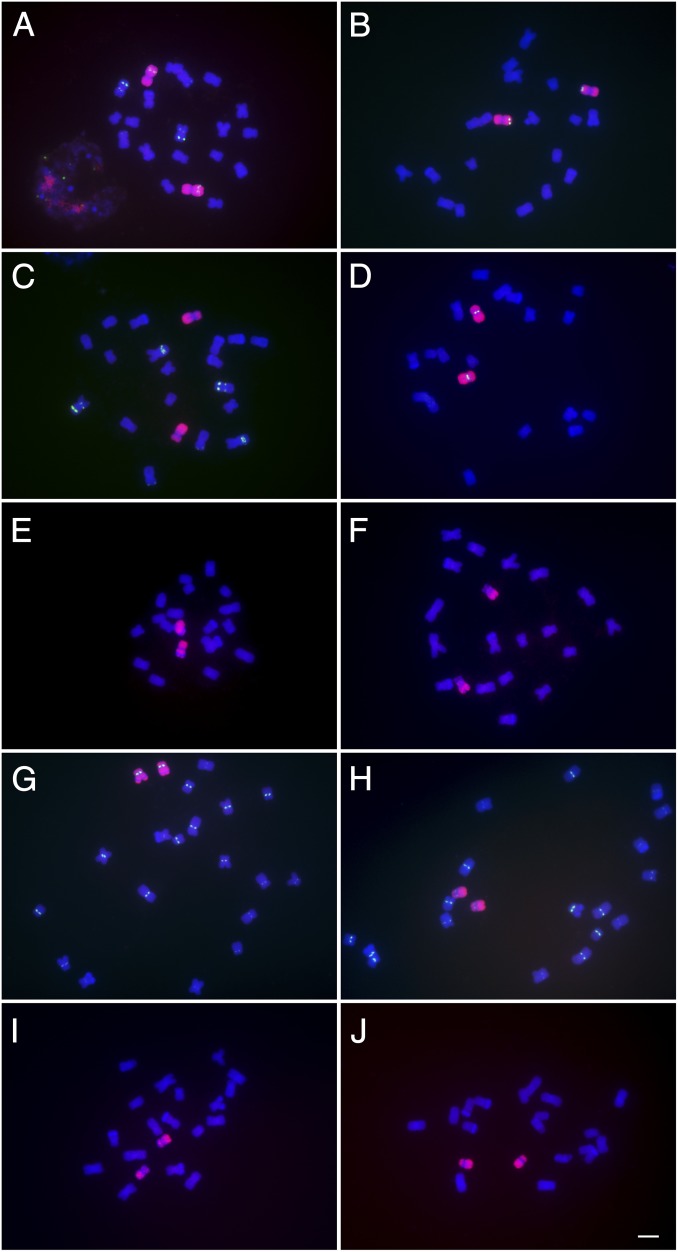
Fig. 1.
Individual oligonucleotide paints for chromosomes 1–10. Each library was labeled with ATTO-550 (red) and probed onto root tip metaphase spreads of inbred line KYS. Chromosomes were labeled with DAPI (blue), which reveals the sites of heterochromatic knobs. The confirmation of chromosome was determined by FITC or 6-FAM counterprobing in green of repetitive elements that are universally characteristic of the respective chromosome (12, 21) or previously characterized for KYS (21). (A) Chromosome 1, counterprobed with TAG microsatellite. Note the interphase nucleus at the Lower Left. (B) Chromosome 2, counterprobed with 5S ribosomal DNA. (C) Chromosome 3 lacks counterprobe of TAG microsatellite. (D) Chromosome 4, counterprobed with Cent4, a repetitive array specific to this chromosome. (E) Chromosome 5, defined by being near metacentric with a large heterochromatic knob in the long arm (gap in painting). (F) Chromosome 6, characterized by the presence of the secondary constriction (NOR). (G) Chromosome 7, counterprobed with CentC, which has a strong signal for chromosome 7 in KYS and defined by a large heterochromatic knob in the long arm. (H) Chromosome 8, counterprobed with CentC, which has a weak signal for chromosome 8 in KYS and no knob in the long arm. (I) Chromosome 9, defined by a heterochromatic knob at the tip of the short arm. (J) Chromosome 10, defined by its acrocentric morphology and absence of heterochromatic knobs. Grayscale images are presented in SI Appendix, Fig. S2. (Scale bar, 5 µm.)